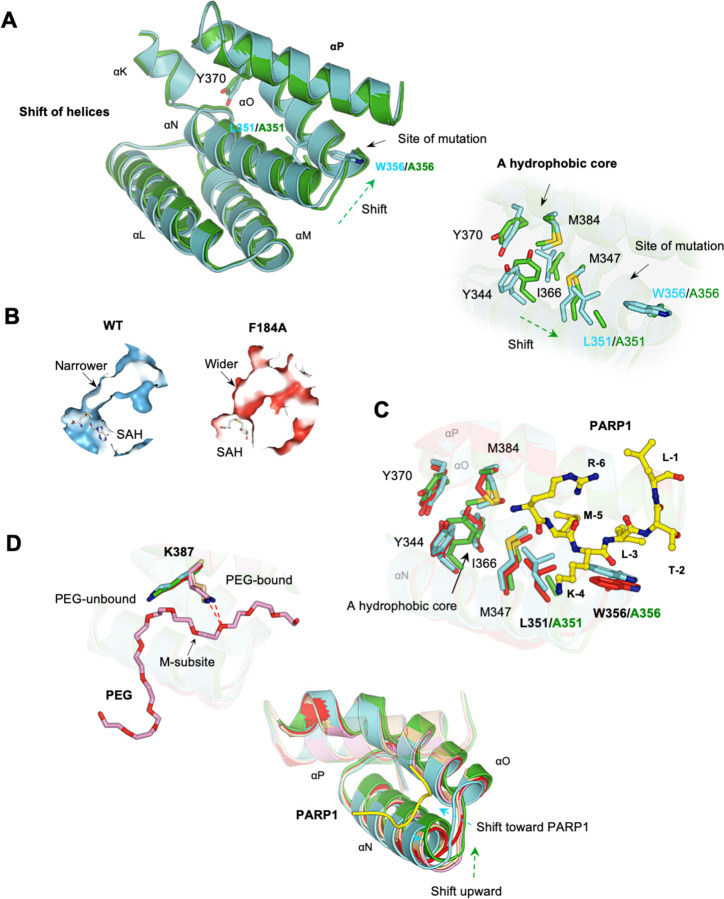
Fig. 4. Structural comparison of wild-type and mutant SMYD2.
(A) Minor structural differences at the secondary binding site between SMYD2-PARP1 (cyan) and SMYD2-L351A/W356A (green). Left: shift of helices. Right: shift of a hydrophobic core. (B) The widened target lysine access channel in SMYD2F184A. (C) Superposition of SMYD2-PARP1 (cyan), SMYD2-F184 (red), and SMYD2-L351A/W356A (green) at the secondary binding site. (D) The structural flexibility of the secondary binding site. Left: PEG-bound and PEG-unbound structures have different K387 conformations. Right: the unique structural changes upon PARP1 binding, PEG binding, and point mutation.