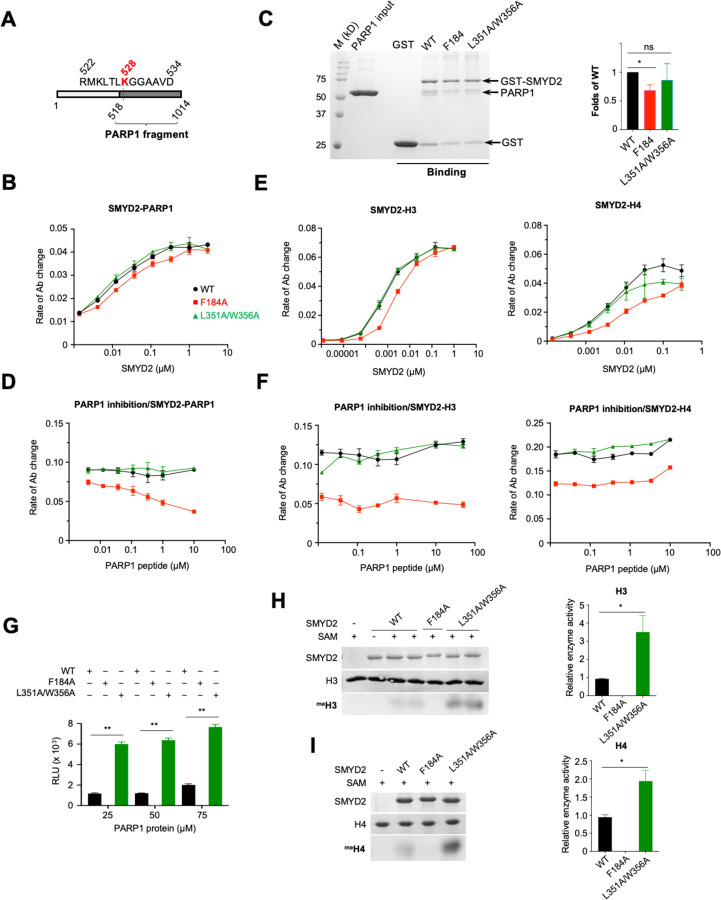
Fig. 6. The binding specificity and regulatory nature of the secondary binding site.
(A) The construct of a PARP 1 protein fragment (PARP1(518–1014)). (B) ELISA and (C) GST pulldown analysis of the binding between SMYD2 proteins and PARP1(518–1014). (D) Inhibition of SMYD2-PARP1(518–1014) interaction by the PARP1 peptide. (E) ELISA analysis of the binding between SMYD2 proteins and histone H3 (left) and histone H4 (right). (F) Inhibition of SMYD2-H3 (left) and SMYD2-H4 (right) interactions by the PARP 1 peptide. (G) The methyltransferase activity of SMYD2 proteins on PARP 1(518–1014) assayed by the MTase-Glo methyltransferase assay. The methyltransferase activity of SMYD2 proteins on (H) H3 and (I) 114 assayed by the antibody-based methyltransferase assay. One (*) and two (**) indicate statistical significance with p-values ? 0.05 and 0.001, respectively.