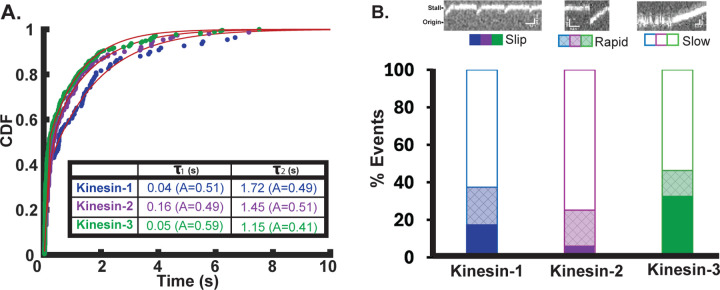
Figure 4. Reattachment Rates for Kinesin-1, -2 and -3.
(A) Cumulative distribution of reattachment times for each motor fit to a bi-exponential by least squares. Kinesin-1 (blue) has a fast reattachment time constant of 0.04 s (95% CI [0.03, 0.04]), and a slow time constant of 1.72 s [1.65, 1.79] with (N=109 events). Kinesin-2 (purple) has a fast reattachment time constant of 0.16 s [0.15, 0.18], and a slow time constant of 1.45 s [1.34, 1.56] (N=151). Kinesin-3 (green) has a fast reattachment time constant of 0.05 s [0.04, 0.05]), and a slow time constant of 1.15 s [1.10, 1.20] (N=254). (B) Bar plot showing the fraction of slip, fast, and slow rebinding events for each motor, with example kymographs for each (top). Solid bars indicate slips during stall, where the motor resumes a new ramp within a single frame (~40 ms). Crosshatched shading indicates rapid reattachment events, where the motor falls back to within 400 nm of origin and initiates a new ramp within 100 ms. Open bars indicate slow reattachment events where motors detach from ramp or stall and fluctuate around the origin for >100 ms before rebinding and initiating a new ramp.