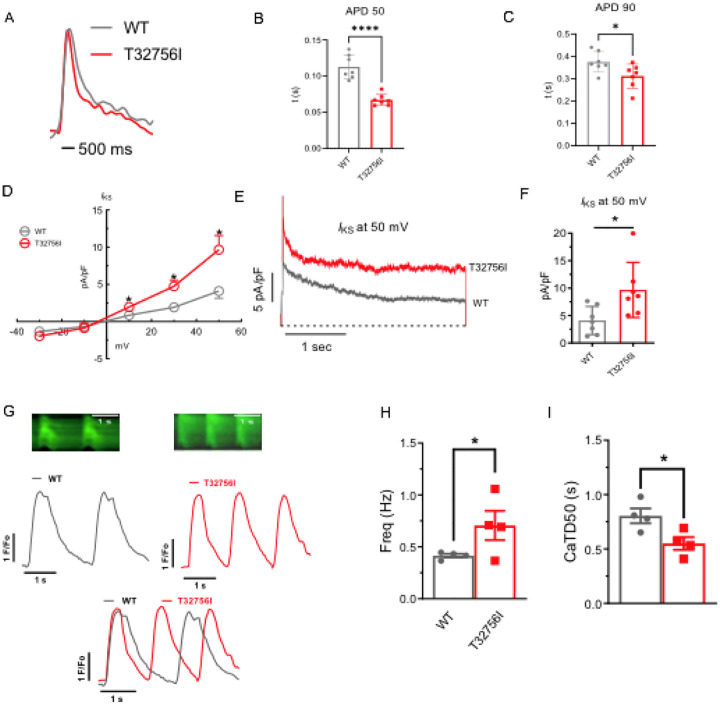
Figure 3: Effect of T32756I on action potential (AP) and calcium-handling in iPSC-aCMs.
(A-C) Representative optical AP recordings of WT and TTN-T32756I showing reduction of AP duration (APD) at the 50% (APD50) (B) and 90% (APD90) repolarization (C). (D) Current-voltage (I-V) curves of the slow delayed rectifier potassium current (Iks) in WT and TTN_T32756I iPSC-aCMs. control (n=7) (E-F) Comparison of Iks current density at 50 mV (mean ± SEM). N.s.; P>0.05; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001. (G) Representative tracings of spontaneous calcium transients of WT and TTN-T32756I iPSC-aCMs. (H-I) Calcium kinetics show that the TTN-T32756I iPSC-aCMs have increased frequency (B) and decreased transient durations (I) compared with the WT iPSC-aCMs.