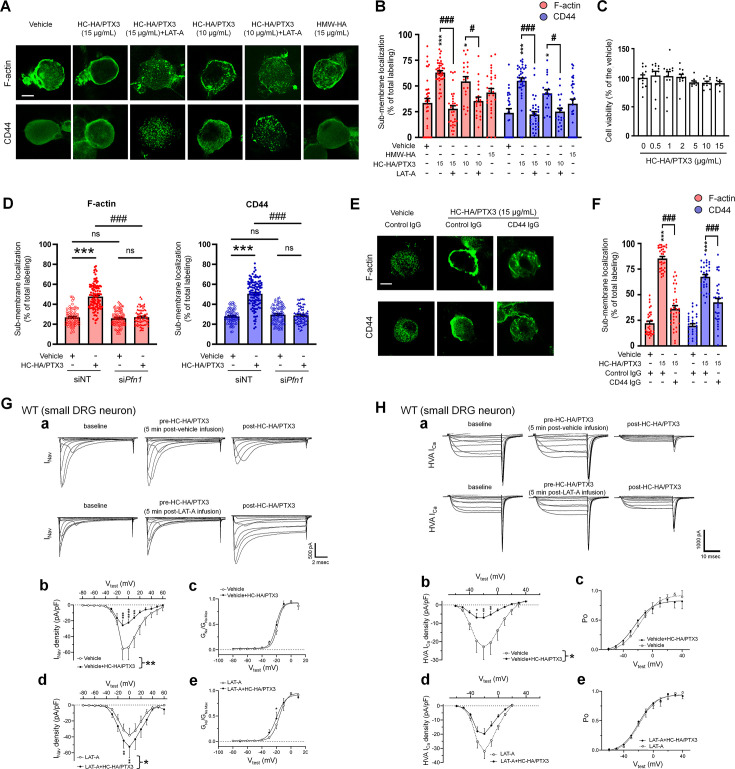
Figure 5. Heavy chain-hyaluronic acid/pentraxin 3 (HC-HA/PTX3) induced cytoskeletal rearrangement which contributed to its inhibition of INav and HVA-ICa.
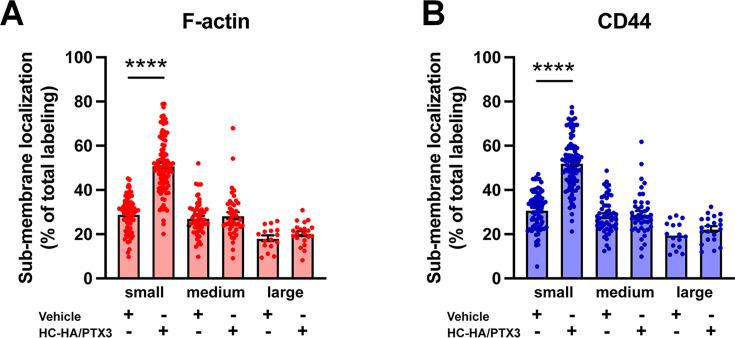
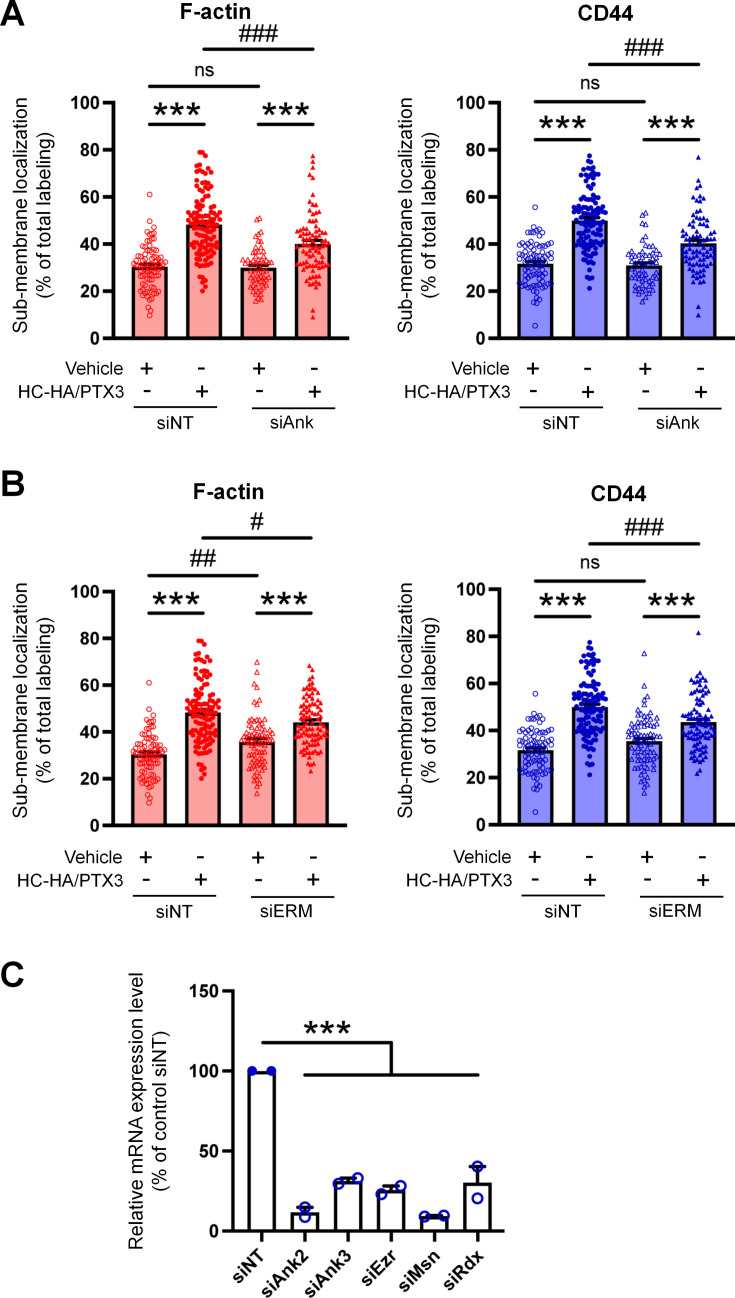
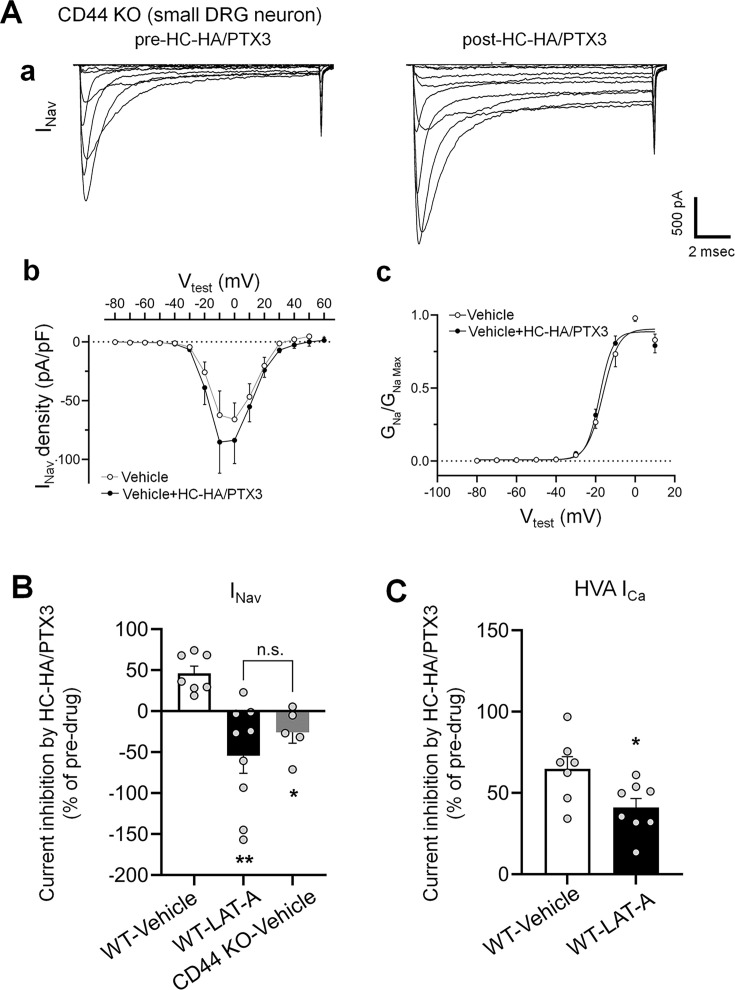
(A) Example images show the distribution of F-actin and CD44 staining in small dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons of wild-type (WT) mice. Neurons were treated with bath application of vehicle (saline), high-molecular-weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA) (15 μg/ml), HC-HA/PTX3 (10, 15 μg/ml), or HC-HA/PTX3 (10, 15 μg/ml) combined with Latrunculin A (LAT-A, 1 μM) for 45 min. Scale bar: 5 μm. DRG neurons were categorized according to cell body diameter as <20 μm (small), 20–30 μm (medium), and >30 μm (large). (B) Quantification of sub-membranous F-actin polymerization and translocation of CD44 in small WT DRG neurons after drug treatment. N = 30–80/group. (C) Proliferation MTT assay showed a lack of neuronal toxicity from 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, and 15 μg/ml HC-HA/PTX3, compared to vehicle (100% viable cells). N = 6–12 repetitions/group. (D) Quantification of sub-membranous F-actin polymerization and translocation of CD44 in small DRG neurons. DRG neurons were electroporated with siRNA targeting Pfn1 (siPfn1) or non-targeting siRNA (siNT, control). Neurons were treated with vehicle (saline) or HC-HA/PTX3 (10 μg/ml) for 45 min. N = 70–111/group. (E) Changes in the sub-membrane distribution of F-actin and CD44 in WT DRG neurons treated with vehicle + control IgG (2 µg/ml), HC-HA/PTX3 (15 μg/ml) + control IgG (2 µg/ml), or HC-HA/PTX3 (15 μg/ml) + CD44 IgG (2 µg/ml) for 45 min. Scale bar: 5 μm. (F) Quantification of the sub-membrane F-actin and CD44 labeling in each group. (G) Infusion of LAT-A attenuated the inhibition of INav by HC-HA/PTX3 in WT DRG neurons. (a) Representative traces of INav after 5 min infusions of vehicle (top row) or LAT-A (bottom row, 0.5 nM) through the recording electrode, followed by bath application of HC-HA/PTX3 (10 µg/ml). Lumbar DRG neurons were harvested on Days 2–3 after plantar-incision. (b) There was a significant interaction between the variation produced by HC-HA/PTX3 (10 µg/ml) and test voltages (VTest) applied in vehicle-infused neurons, resulting in an overall INav inhibition (F(14,90) = 3.29, ***p < 0.001), and significantly decreased INav density (pA/pF) from VTest = −10 to +10 mV, as compared to pre-HC-HA/PTX3 treatment. N = 7/group. (c) HC-HA/PTX3 did not alter GNa/GNa max across the test voltages (F(9,60) = 0.44, p = 0.9) in vehicle-infused neurons. N = 7/group. (d) There was a significant interaction between the variation produced by HC-HA/PTX3 (10 µg/ml) and VTest applied in LAT-A-infused neurons, resulting in overall INav increase (F(14,120) = 1.87, *p < 0.05) and increased INav density (pA/pF) from VTest = −10 to 0 mV, as compared to pre-HC-HA/PTX3. N = 9/group. (e) HC-HA/PTX3 significantly increased the GNa/GNa max at VTest = −20 mV in LAT-A-infused neurons (*p < 0.05, N = 9/group). (H) LAT-A attenuated the inhibition of HVA-ICa by HC-HA/PTX3 in WT DRG neurons. (a) Representative traces of HVA-ICa in small WT DRG neurons after 5 min infusions of vehicle (top row) or LAT-A (bottom row, 0.5 nM), followed by bath application of HC-HA/PTX3 (10 µg/ml). (b) In vehicle-infused neurons, HC-HA/PTX3 (10 µg/ml) significantly decreased HVA-ICa (F(1,12) = 6.52, *p = 0.02) and HVA-ICa conductance (I/Imax) from VTest = −40 to +10 mV, as compared to pre-HC-HA/PTX3. N = 7. (c) HC-HA/PTX3 did not alter the channel open probability (Po) in vehicle-infused neurons (p = 0.82, N = 7). (d) In LAT-A-infused neurons, HC-HA/PTX3 only modestly reduced HVA-ICa conductance across test voltages applied (F(1,12) = 0.27, p = 0.6, N = 8). (e) HC-HA/PTX3 did not alter Po in LAT-A-infused neurons (p = 0.94, N = 8). Data are mean ± SEM. (B–D, F) One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 versus indicated group. (G, H) Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 versus vehicle infusion or LAT-A infusion group.