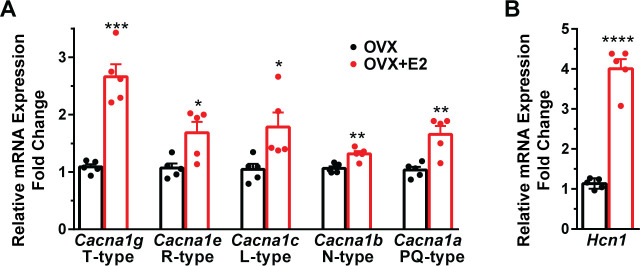
Figure 4. E2 increases the mRNA expression of volatge-activated Ca2+ channels and Hcn1 channels in Kiss1ARH neurons.
(A) E2 increases the expression of low and high voltage-activated calcium channels in Kiss1ARH neurons. Kiss1ARH neurons (three 10-cell pools) were harvested from each of five vehicle- and five E2-treated, OVX females to quantify ion channel mRNA expression of low and high voltage-activated calcium channels as described in the ‘Materials and methods’. The analysis included T-type (Cacna1g) low voltage-activated, as well as the following high voltage-activated channels: R-type (Cacna1e), L-type (Cacna1c), N-type (Cacna1b), and P/Q-type (Cacna1a) calcium channels. Interestingly, all of these channels were upregulated with E2 treatment, which significantly increased the whole-cell calcium current (see Figure 5). Bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM, with data points representing individual animals (oil versus E2, unpaired t-test for Cacna1g, t(8) = 7.105, ***p=0.0001; for Cacna1e, t(8) = 3.007, *p=0.0169; for Cacna1c, t(8) = 2.721, *p=0.0262; for Cacna1b, t(8) = 4.001, **p=0.0039; for Cacna1a, t(8) = 4.225, **p=0.0028). (B) The same Kiss1ARH neuronal pools were also analyzed for mRNA expression of Hcn1 ion channels, and E2 also increased the expression of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic-nucleotide gated Hcn1 channels in Kiss1ARH neurons. Hcn1 channel mRNA expression was the most highly upregulated by E2 treatment in Kiss1ARH neurons. The expression values were calculated via the ΔΔCT method, normalized to Gapdh and relative to the oil control values (oil versus E2, unpaired t-test, t(8) = 11.450, ****p<0.0001).