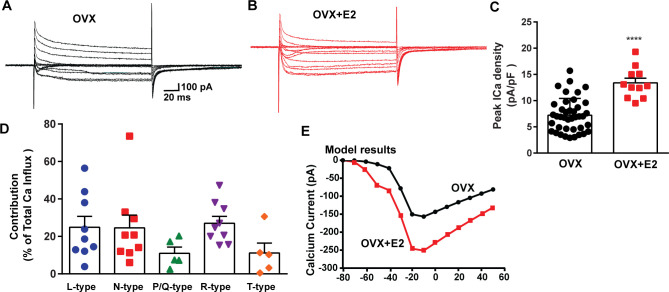
Figure 5. E2 treatment (positive feedback regimen) increases the Ca2+ currents in Kiss1ARH neurons.
(A, B) Ca2+ currents in Kiss1ARH neurons with the same membrane capacitance from oil-treated (A) or E2-treated (B) animals. (C) The maximum peak currents were measured at –10 mV. The current amplitudes were normalized to the cell capacitance in all cases to calculate current density. The bar graphs summarize the density of Ca2+ current in Kiss1ARH neurons from oil-treated and E2-treated animals. The mean density was significantly greater in E2-treated (13.4 ± 0.9 pA/pF, n = 11) than in oil-treated OVX females (7.2 ± 0.5 pA/pF, n = 40) (unpaired t-test, t(49) = 5.75, ****p<0.0001). (D) Relative contribution of voltage-gated calcium currents in Kiss1ARH neurons from OVX, E2-treated mice. The maximum peak currents were measured at –10 mV. The proportions of Ca2+ currents inhibited by nifedipine (L type), ω-conotoxin GVIA (N type), ω-agatoxin IVA (P/Q), SNX-482 (R type), and TTA-P2 (T type). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, with data points representing individual cells. (E) The modeling predicts that E2-treated, OVX females exhibit a significantly greater inward Ca2+ current (red trace) than the vehicle-treated females (black trace). The conductance of the modeled voltage-gated calcium current (L-, N-, P/Q-, and R-type) is set to 2.1 nS in the OVX state and 2.8 nS in OVX + E2 state, while for the T-type is set to 0.66 nS in the OVX state and 5 nS in OVX + E2 state.