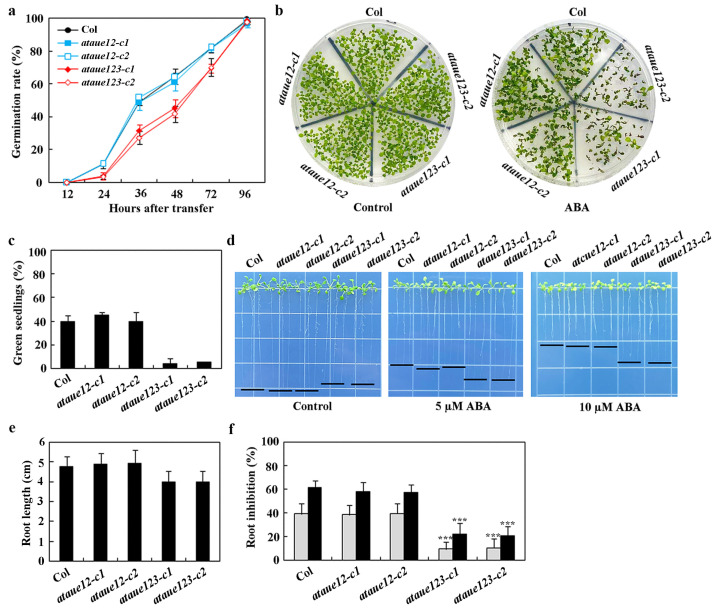
Figure 6.
Effects of ABA on seed germination, cotyledon greening, and root elongation in Col wild-type, ataue12 double mutants, and ataue123 triple mutants. (a) Seed germination assay. Surface-sterilized seeds of Col wild-type, ataue12 double mutants, and ataue123 triple mutants were plated on 1/2 MS plates with or without 1 μM ABA. Plates were kept at 4 °C in the dark for 2 days, then transferred to a growth room. The number of germinated seeds was counted at the indicated times, and germination percentages were calculated. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three replicates. (b) Cotyledon greening assay. Surface-sterilized seeds were plated as above. Images were taken 15 days after transfer to the growth room. (c) Quantitative analysis of green seedlings. The number of seedlings with green cotyledons was counted, and percentages were calculated. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three replicates. (d) Root elongation assay. Surface-sterilized seeds were plated on 1/2 MS plates, kept at 4 °C in the dark for 2 days, then grown vertically for 3 days in a growth room. Seedlings were transferred to control plates or plates containing 5 μM and 10 μM ABA and grown for an additional 7 days before imaging. (e) Root length measurements. Root lengths of seedlings were measured after imaging. Data are presented as means ± SD of 26–38 seedlings. (f) Quantitative analysis of root elongation inhibition by ABA. Root lengths of newly elongated roots were measured after imaging, and the percentage of inhibition was calculated for ABA concentrations of 5 μM (gray) and 10 μM (black). Data are presented as means ± SD of 26-38 seedlings. Significantly different from that of the Col wild-type seedlings (*** p < 0.001).