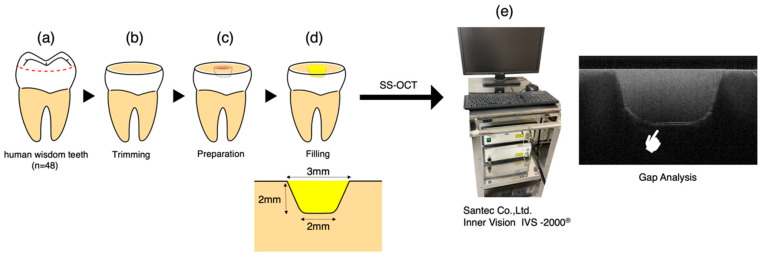
Figure 2.
Specimen preparation for gap analysis: (a) Forty-eight sound extracted human wisdom teeth were selected. (b) After sectioning the occlusal enamel with a precision diamond saw, the surface layer was polished with 800-grit SiC paper to create a flat dentin surface. (c) Tapered cylindrical cavities (upper diameter: 3 mm, lower diameter: 2 mm, depth: 2 mm, no pulp exposure) were prepared using a high-speed handpiece with a diamond bur under water cooling. The samples were randomly divided into four groups (12 samples each) according to the materials used. (d) The cavities were treated following the manufacturers’ instructions for adhesive application and resin core build-up procedures. (e) Samples were observed using SS-OCT, and 2D images were captured. Each sample was fixed on the precise head stage of the SS-OCT, and a scanning laser beam was directed perpendicularly onto the restoration surface.