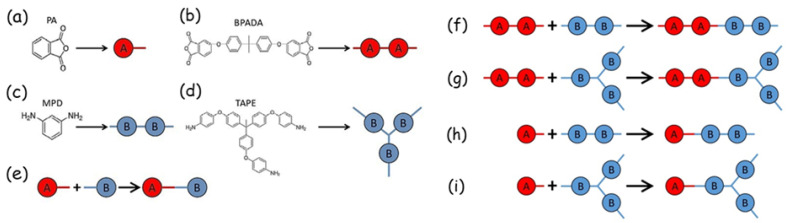
Figure 10.
(a–d) The four types of monomers constituting a branched polyetherimide (PEI), used as models in the MC simulations, include: phthalic anhydride (PA), 4,4-bisphenol A dianhydride (BPADA), m-phenylenediamine (MPD), and tris[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl] ethane (TAPE) (the latter containing three terminals). The B bead represents a full functional group containing one amine, and the A bead represents a functional group containing a carboxylic anhydride. (e) The condensation reaction between an amine group and a carboxylic anhydride one, taking place in the polymerization of PEIs, is represented by the formation of a bond between beads A and B. (f–i) The polymerization of branched PEIs is represented by the following four reactions: (f) BPADA + MPD (see (b,c) above); (g) BPADA + TAPE (see (b,d) above); (h) PA + MDP (see (a,c) above); (i) PA + TAPE (see (a,d) above) (adapted from [89]).