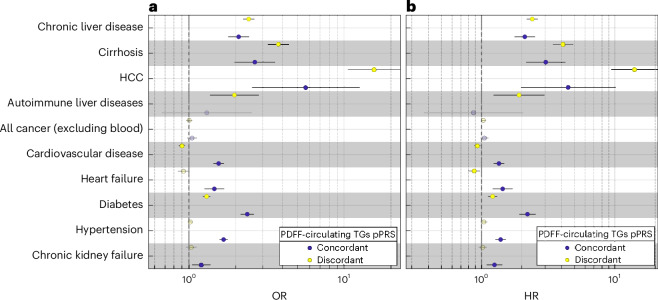
Fig. 3. Partitioned polygenic risk scores identify a steatotic liver-specific disease and a systemic MASLD.
a,b, The case–control (a) and prospective (b) association between two PDFF-circulating TGs pPRS and liver-related, cardiometabolic and chronic kidney failure traits in the UK Biobank. Effect plot of the association between concordant and discordant PDFF-circulating TGs PRS with each disease was tested using either logistic (a) or Cox proportional hazard (b) regression analysis adjusted for BMI, age, sex, age × sex, age2 and age2 × sex, first ten genomic principal components and array batch. The x axis shows either the odds ratio (OR) or hazard ratio. All association analyses have been performed after excluding individuals with available PDFF (n = 36,394). Error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals from the regression models. Full summary statistics have been reported in Supplementary Table 18. P values were two-sided and not corrected for multiple hypothesis testing. TG, triglyceride.