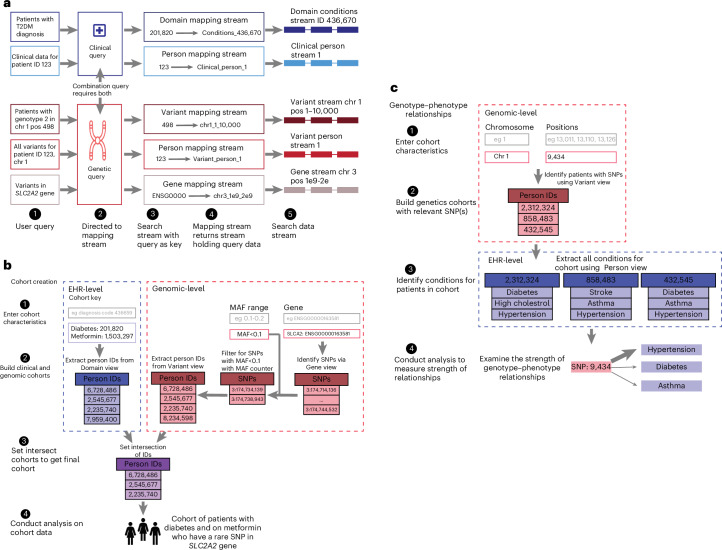
Fig. 2. Indexing and analysis on PrecisionChain.
a, Mapping stream indexing. Based on the users’ query, search keys are directed to the appropriate stream. A mapping stream is created for every view. Entries in the mapping stream follow a Key:Value structure (Key is the user’s input; Value is the stream where the data are stored). b, Cohort creation. Users input desired clinical characteristics, genes of interest and a MAF filter into the search function. Using the EHR-level ‘Domain view’, patient IDs for those that meet clinical criteria are identified. Using the Genetic-level ‘Gene, MAF counter and Variant views’, the appropriate variants are identified, and patient IDs with those variants are extracted. A set intersection of the two cohorts is done to create a final cohort, which can be analyzed further. c, Genotype–phenotype relationships. Users input variants of interest into the search function. Using the Genetic-level ‘Variant view’, IDs for patients with that variant(s) are extracted. All diagnoses for each patient are retrieved using the EHR-level ‘Person view’. The strength of relationship between each SNP and condition can be examined. ‘Gene view’ can give further information on what genes are carrying the variants, linking the clinical information to detailed genetic information (chr, chromosome; pos, position).