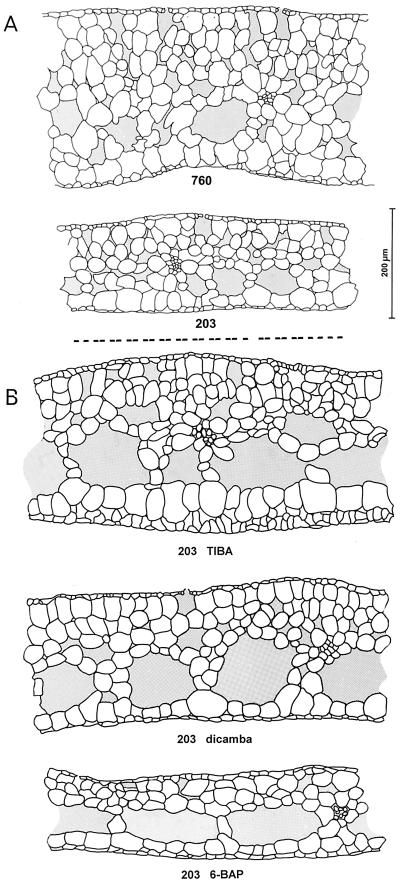
Figure 2.
Frond architecture of S. punctata ecotypes. Plants were raised phototrophically on Hutner's medium (A; 203 and 760) or on Hutner's medium (B) supplemented with 1 μm TIBA (203 TIBA), 10 μm dicamba (203 dicamba), or 1 μm 6-BAP (203 BAP). Fresh fronds were dissected with a microtome and 20- to 40-μm-thick cross sections were studied using a light microscope. Sections reveal the upper epidermis with stomata, spongy photosynthetic tissue containing large intercellular spaces, and vascular bundles and a thin lower epidermis. The average frond thickness (±se of the mean) was 254 ± 9 μm (760), 181 ± 9 μm (203), 288 ± 30 (203 TIBA), 241 ± 3 (203 dicamba), and 161 ± 8 (203 BAP). Statistical analysis (Student's t test) reveals the significance of the differences between 203 and 760 (P < 0.01) and between 203 and 203-dicamba and 203-TIBA (P < 0.01). Values reflect the analysis of three to 14 leaves, with five measurements per leaf. Pictures are representative cross sections. The black bar represents a length of 200 μm.