Central Illustration 1.
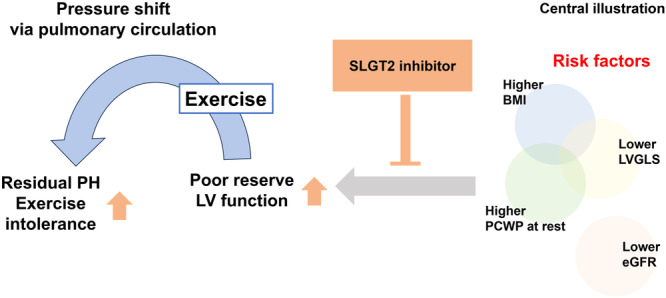
Effect of SGLT2 inhibition on exercise‐induced post‐capillary pulmonary hypertension. In this study, patients with exercise‐induced post‐capillary PH (post‐EIPH) exhibited higher BMI, increased PAWP at rest, and lower LVGLS. Those risk factors would lead to poor reserve of left ventricular function, which exacerbate pulmonary hypertension during exercise. This study demonstrated that SGLT2 inhibitor treatment alleviated haemodynamic abnormalities and exercise intolerance associated with post‐EIPH. BMI, body mass index; CO, cardiac output; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; LV, left ventricular; LVGLS, left ventricular global longitudinal strain; PCWP, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; PH, pulmonary hypertension; SGLT2, sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2.
