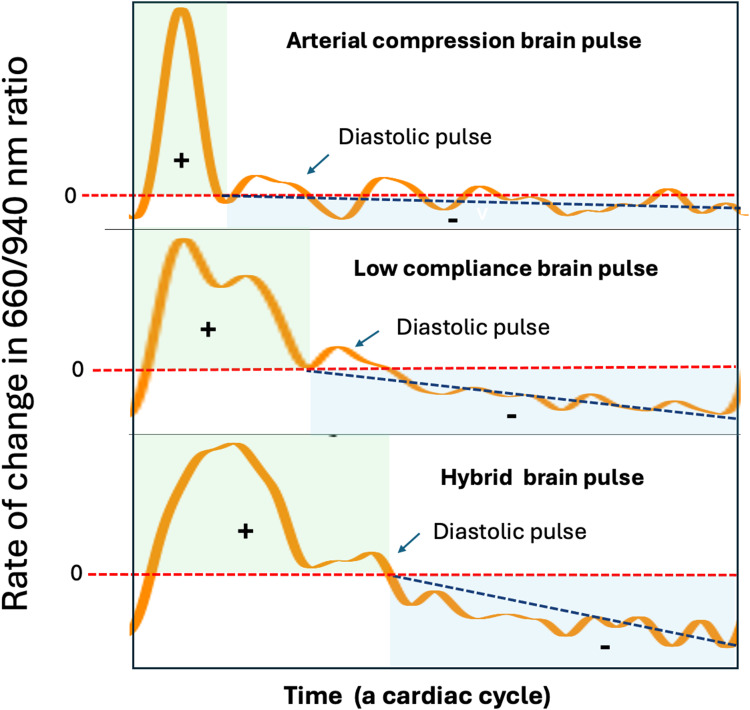
Figure 9.
Classes of brain pulses and the rate of change in the 660/940 nm ratio. The rate of change in the 660/940 nm ratio, may represent the speed and direction of change in blood oxygen levels during a cardiac cycle. The Y axis represents the direction and rate of change. A rate greater than 0 (red serrated line) represents an increase in oxygen levels, while less than 0 a fall in oxygen levels. The duration of increasing oxygen levels is delineated by the green shaded area. The duration of the fall in oxygen levels is delineated by the blue shaded area. For the Arterial brain compression pulse there is a rapid and steep increase in the 660/940 ratio, thereafter there is a long gentle fall. The gentle slope (or rate of fall) is indicated by the black serrated line. In comparison for the Low compliance brain pulse the rate of increase in 660/940 ratio is less steep, and the duration of increase longer, while the rate of fall in diastole is steeper and the duration of fall shorter. In comparison to the Low compliance brain pulse for the Hybrid brain pulse the rate of increase is less steep, and the duration of increase longer, while the rate of fall is steeper and the duration of fall shorter. These findings suggest that compared to the normal arterial brain pulse cerebral blood flow and oxygen levels are lower in the low compliance brain pulse and even lower again in the Hybrid brain pulse. Of note the Diastolic pulse is associated with a brief increase in the 660/940 ratio.