Fig. 5. Sequence and activity of eIF3a promoter.
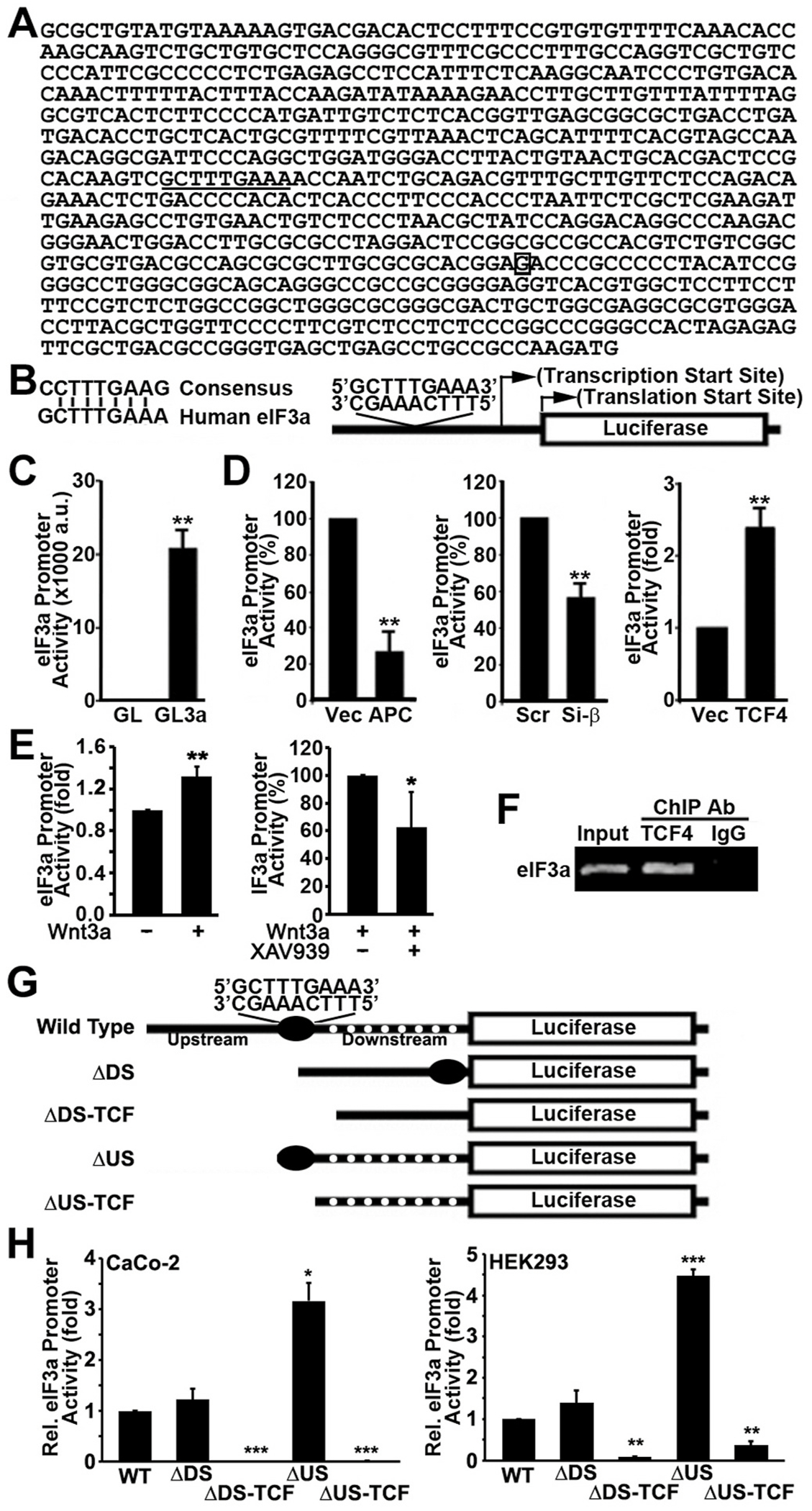
A. Promoter sequence of human eIF3a. The putative LEF/TCF binding site GCTTTGAAA (underlined) is 279 bases upstream of the transcription start site (boxed G) and 426 bases upstream of the translation initiation codon ATG. B. Comparison between the consensus and the putative LEF/TCF binding sequences in human eIF3a gene and the schematic diagram of the luciferase reporter construct. C-D. Basal eIF3a promoter activity and its regulation by APC, β-catenin, and TCF4. Promoter construct (GL3a) shown in panel B along with a promoter-less control construct (GL) were transiently transfected into CaCo-2 cells (C) or CaCo-2 cells with over-expression of APC, TCF4 or with β-catenin knockdown (D) for determination of luciferase activity. Vector-transfected controls for APC and TCF4 overexpression or scrambled siRNA control for β-catenin knockdown were also tested, β-galactosidase was used to control transfection efficiency. a.u. = arbitrary units. E. Effect of Wnt3a and tankrase inhibitor on the promoter activity of eIF3a in HEK293 cells. F. ChIP assay of eIF3a promoter using TCF4 antibody or control normal IgG. G. Schematic drawing of deletion constructs of eIF3a promoter sequence. H. Relative promoter activity of wild-type and deletion mutant eIF3a promoters in CaCo-2 and HEK293 cells. (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05).
