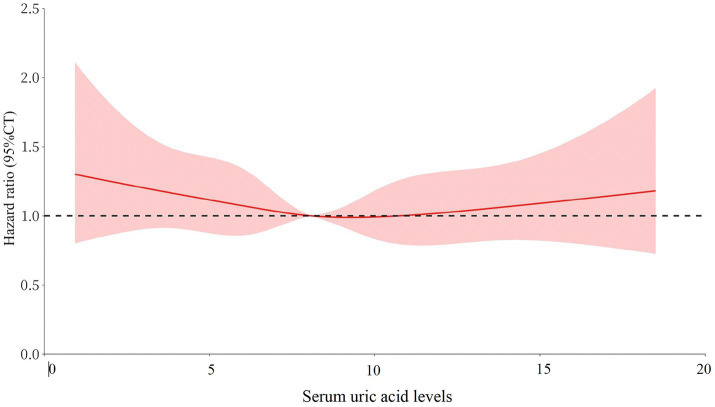
Figure 4.
The form of association between the serum UA levels and cardiovascular-related mortality using restricted cubic splines There was a trend toward a higher mortality risk at both lower and higher serum UA levels after adjusting for age, sex, dialysis vintage, diabetes mellitus, body mass index, lean tissue index, Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index, hemoglobin, albumin, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, total cholesterol, triglyceride, serum creatinine, and UA-lowering agents. However, this association did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.12).