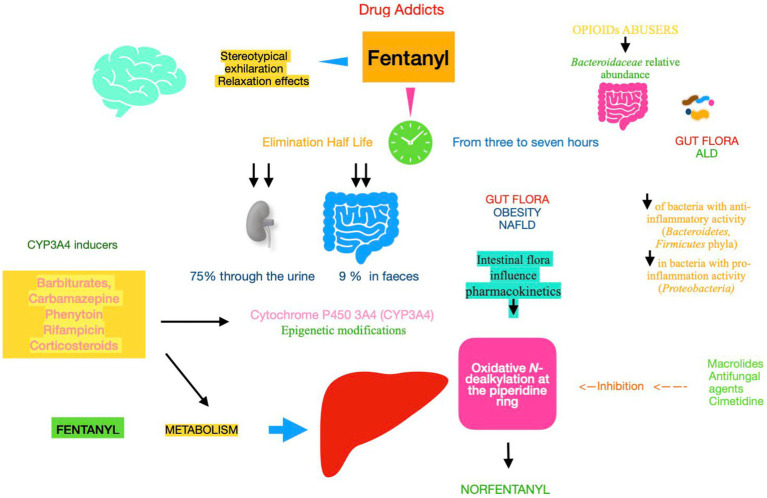
Figure 2.
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of fentanyl Fentanyl metabolism and elimination (half-life), both of them, play an important role in determining drug pharmacokinetics and assessing their efficacy and its adverse effects. Gut microbiota plays a key role during enterohepatic circulation along the drug absorption phase and mainly through various microbial enzymatic reactions in the gut. Fentanyl is 99% N-dealkylated to norfentanyl by cytochrome P450. Utilizing a proteomics approach to quantify the protein expression of CYP3A4 and related enzymes, the results suggest that NAFLD is associated with the decreased hepatic CYP3A4 activity. Epigenetic changes in CYP genes would lead to inter-individual differences in drug responses. Understanding epigenetic mechanisms can help reduce toxicity for drugs metabolized by CYP enzymes. NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ALD, alcoholic liver disease; CYP, cytochrome P450 enzyme.