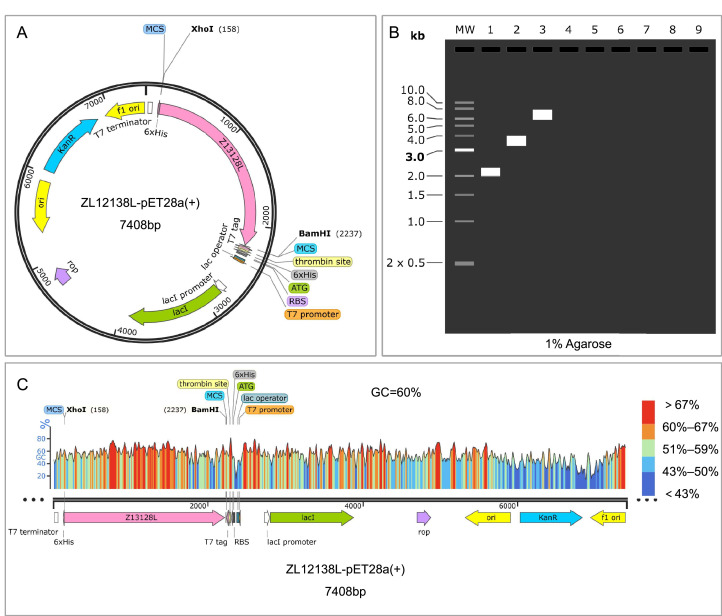
Fig. 7.
Codon optimization and recombinant plasmid construction of the ZL12138L vaccine. (A) Codon optimization and plasmid construction. Computational methods were used to optimize the codons of the ZL12138L vaccine gene for increased expression efficiency in E. coli. The optimized gene sequence was subsequently inserted into the pET28a plasmid using XhoI and BamHI restriction sites. The resulting recombinant expression plasmid, named ZL12138L-pET28a(+), encompasses vital elements, including the T7 promoter, lac operator, ribosome binding site (RBS), 6 × His tag, and the multiple cloning site (MCS). (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis simulation. The SnapGene software was employed to simulate agarose gel electrophoresis to validate the construction of the recombinant plasmid. Lane 1 represents the molecular weight marker (ZL12138L), lane 2 shows the uncut pET-28a(+) plasmid, and lane 3 displays the ZL12138L-pET28a(+) recombinant plasmid, indicating the successful insertion and expected molecular sizes. (C) GC content analysis. The GC content of the codon-optimized ZL12138L vaccine gene was assessed using SnapGene software, revealing a GC percentage of 60%. The plot illustrates the distribution of GC content across the length of the optimized gene sequence, with regions of varying GC proportions indicated by different colors: blue (low GC), green to yellow (medium GC), and red (high GC).