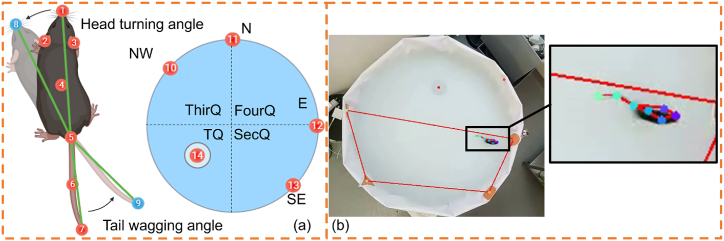
Fig. 1.
Diagram of key point detection and the corresponding visualized results. (a) Diagram illustrating the seven critical points of mouse posture and the five essential environmental points in MMAS. The body parts included the nose, left ear, right ear, body center, tail base, mid-tail, and tail tip (points 1–7 in order). The environmental points included the center of the platform (point 14) and four start locations of NW, N, E and SE (points 10–13 in order). The head turning angle (HTA) was defined as the angle created by the nose’s position before and after the movement, measured between points 1 and 8, with reference to the butt at point 5. The tail wagging angle (TWA) was similarly defined by the positions of the butt (point 5) and the tail tip before and after the movement (points 7 and 9). The division into four quadrants—TQ, SecQ, ThirQ, and FourQ—on the sixth testing day was defined as illustrated. (b) The tracking results visualized in our experimental videos.