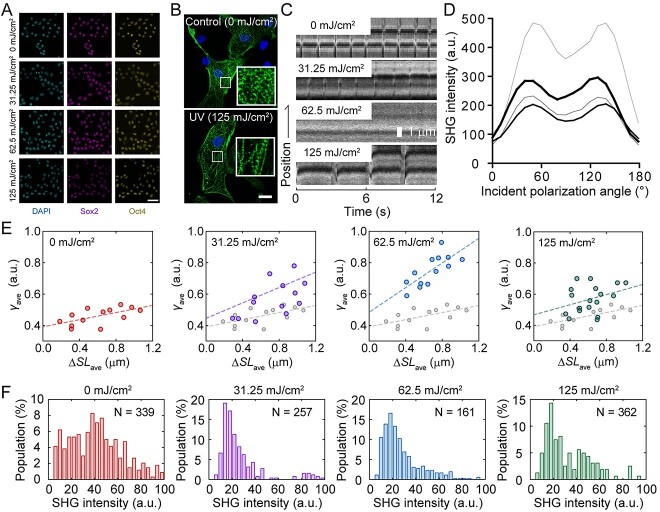
Fig. 3.
Effects of UV irradiation on hiPSCs differentiated into cardiomyocytes. (A) Immunofluorescence image of hiPSCs irradiated with UV. (Left) , DAPI; middle, Sox2; right, Oct4. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence image of cardiomyocytes differentiated from non-irradiated (above) and 125 mJ/cm2 UV-irradiated (below) hiPSCs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Kymograph showing the pulsation of cardiomyocytes differentiated from UV-irradiated hiPSCs observed under an SHG microscope. (D) Dependence of SHG intensity on incident polarization angle without (hairline) or with 31.35 mJ/cm2 (thin line), 62.5 mJ/cm2 (medium line) and 125 mJ/cm2 (thick line) UV irradiation. (E) Relationship between the change in sarcomere length (ΔSL) and γ value. Slack length was set at 1.4 μm. (F) Average SHG intensity histogram of cardiomyocytes derived from iPSCs without and with UV irradiation. Reproduced from Fujita et al., 2023 [54].