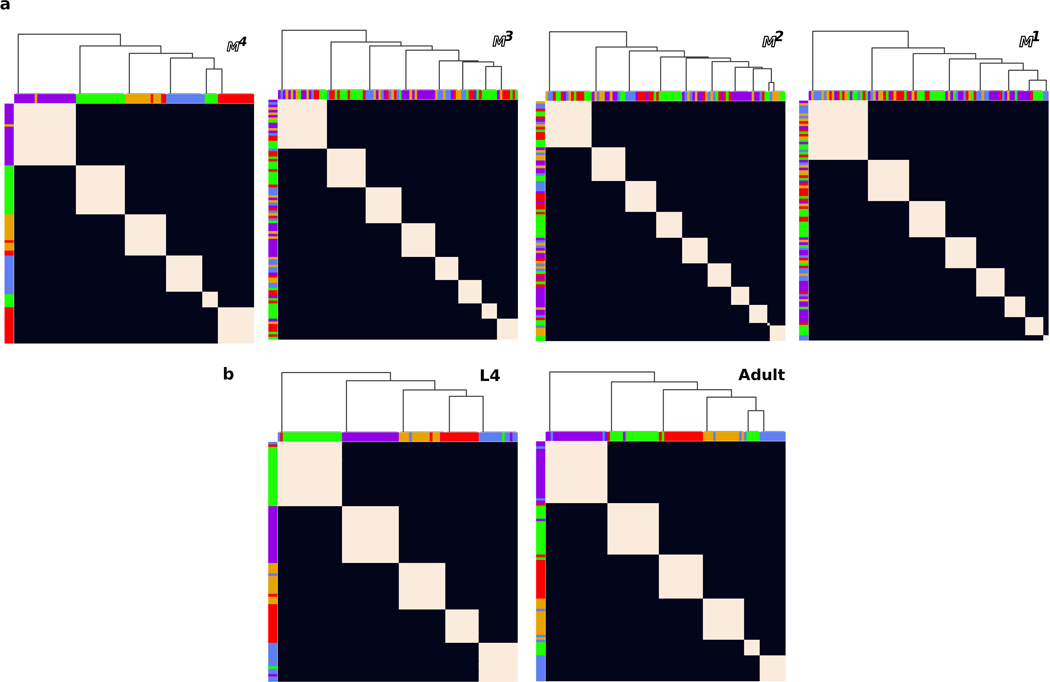
Extended Data Fig. 6. Variable contacts obscure the organization of the nerve ring.
a, Cluster analysis of unperturbed membrane contact datasets , , and . Clustering results for membrane contacts predicted to combine core and variable contacts () and overwhelmingly variable contacts (, ) significantly and increasingly diverge from 5 consensus clusters, indicated by large numbers of small clusters. b, Cluster analysis of (unperturbed) L4 and adult datasets. Both the unperturbed and adult datasets yield 6 clusters rather than the 5 clusters found in the perturbed population models (Figure 1c and Extended Data Fig. 5). The additional cluster results from a split of the taxis cluster into two. This split of the taxis cluster is not observed in either the perturbed or the perturbed Adult dataset, even with half the noise levels observed empirically, indicating that the split is unlikely to be robust across a population of animals. For all cluster frequency matrices: Row and column ordering and colors are the same as the perturbed population dataset (Extended Data Figure 5i). Matrix element (, ) is 1 if cells and cluster together and 0 otherwise. Top: dendrogram of the hierarchical clustering.