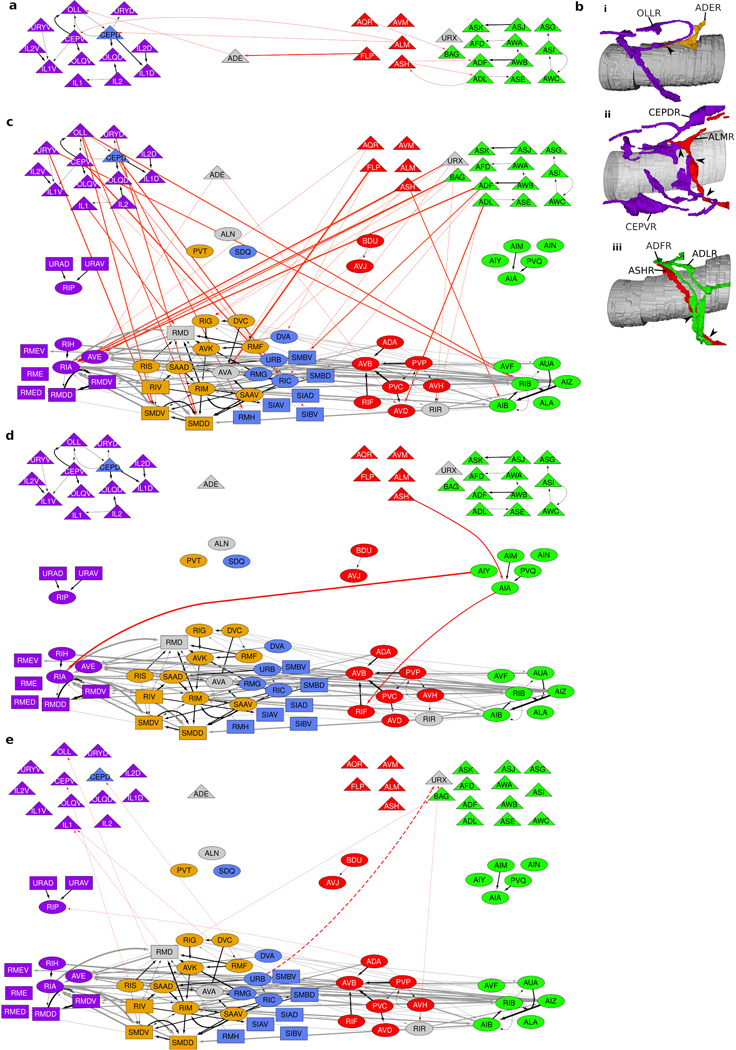
Extended Data Fig. 10. 17% of contacts are not accounted for by the ResNet model.
a, Layer-1 synaptic connectivity across information processing modules in could support distributed sensory computation and integration. 8 (2% of ) contacts occur between sensory cells across different modules. These contacts include: (i) ADE→OLL, (ii) ALM→CEPD/V, (iii) reciprocal contacts between ASH, ADL and AFD. (i) Mechanosensitive48,49 anterior cell OLL loops around intermediate processes, while the processes of ADE extend toward the OLL loop, suggesting a functional role for the more elaborate loop morphology. (ii) Both CEPD and CEPV processes loop around intermediate processes and extend flattened protrusions to meet the ALM processes, where ALM are postsynaptic. CEPD and CEPV respond to head touch50, while ALM respond to both gentle51 and harsh52 body touch, inhibit backward locomotion53 and have been implicated in the habituation of tap response54. (iii) Nociception: ASH, ADE and ADF may coordinate avoidance behaviors between the taxis and avoidance modules55. b, Layer-1 to Layer-3 inter-module feed-forward synaptic connectivity in . 54 (12% of ) contacts are inter-module, originate in Layer 1 and target Layer 3 neurons directly. A small number of taxis and avoidance sensory neurons (ADF and ADL, ASH, URX and BAG) project to all but Laterals in Layer 3; this contrasts with extensive anterior sensory neuron projections that almost exclusively target (sub)lateral Layer-3 interneurons and motoneurons, likely mediating rapid sensorimotor transformations. c, Layer-2 and inter-module feed-forward synaptic connectivity. 3 contacts (1% of ) are inter-module and originate in Layer 2. Notably, Layer-2 taxis AIY neurons synapse onto Layer-3 anterior multi-compartment neurons RIA. d, Inter-module feedback synaptic connectivity in . 9 (3% of ) contacts provide inter-module feedback. Black arrows: synaptic contacts between cells in the same neighborhood. Grey arrows: synaptic contacts between layer 3 cells in different neighborhoods. Red arrows: synaptic contacts not accounted for by the ResNet model. Solid arrows: feed-forward or recurrent (intra-layer) synaptic contacts. Dashed arrows: feedback synaptic contacts.