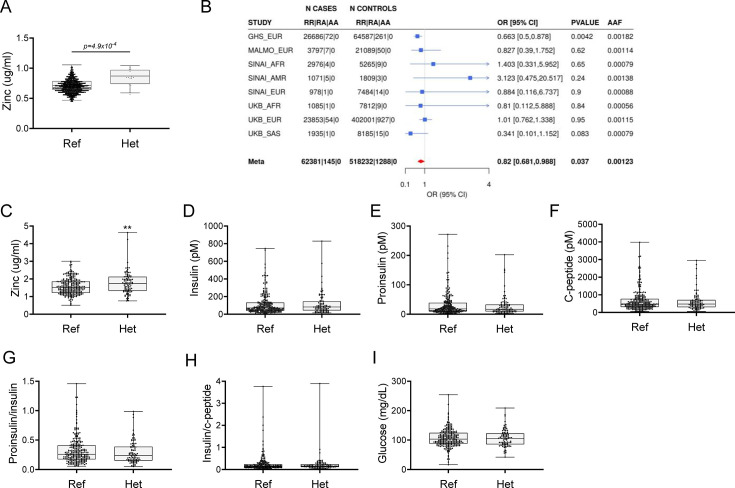
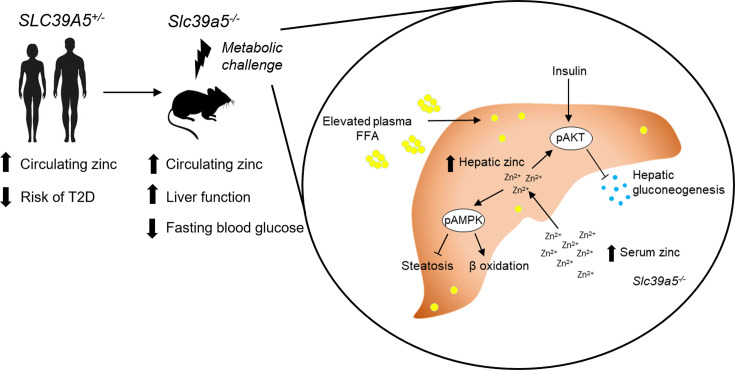
Figure 1. Rare putative LOF (pLOF) variants in SLC39A5 are associated with elevated serum zinc and nominal protection against type II diabetes (T2D).
(A) Serum zinc in carriers of SLC39A5 pLOF variants in the discovery cohort. Controls (Ref; SLC39A5+/+) and heterozygous carriers of pLOF variant alleles in SLC39A5 (Het; SLC39A5+/-). Subject numbers: Ref and Het, respectively: n=5317 and n=15. (B) Trans-ancestry meta-analysis of the association of SLC39A5 pLOF variants with T2D. (C–I) Serum zinc and insulin profile of age, sex and BMI-matched controls in serum call back study. Subject numbers: Ref and Het, respectively: n=246–253 and n=86–91, **p<0.01, unpaired t-test. Numeric data is summarized in Supplementary file 1.