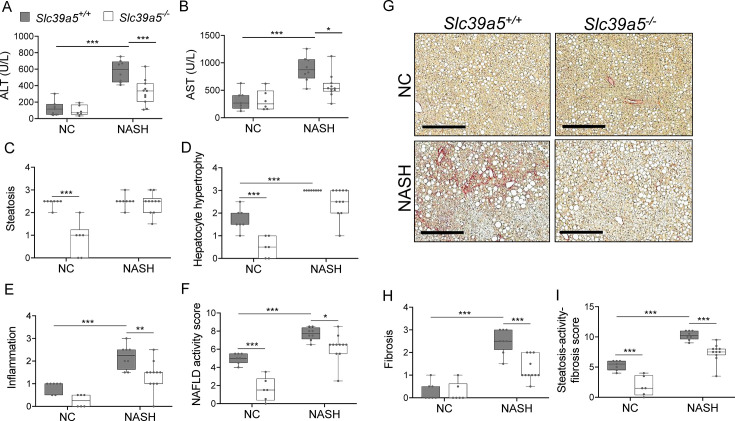
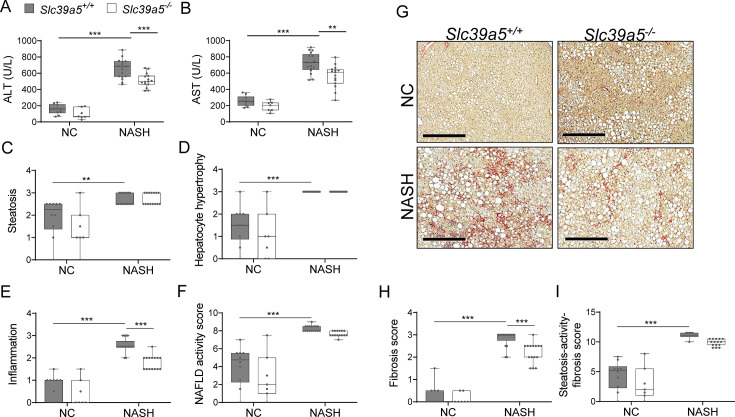
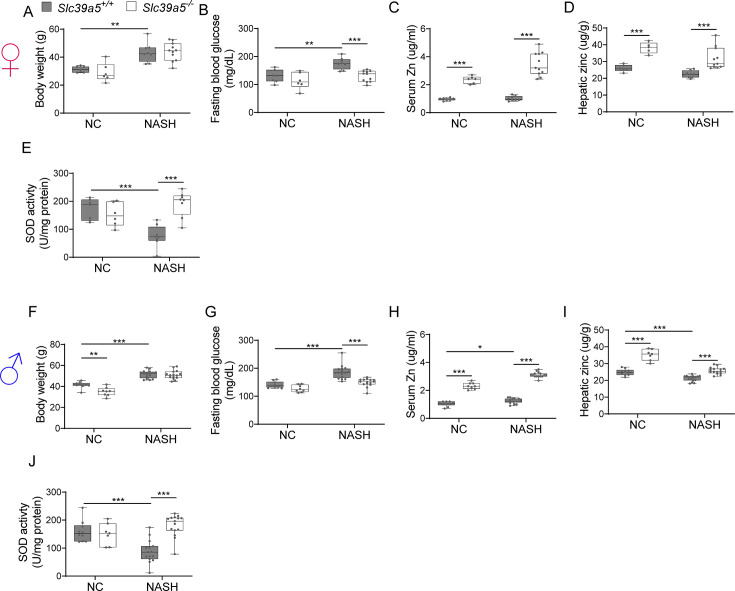
Figure 6. Loss of Slc39a5 improves hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in female mice challenged with diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Slc39a5-/- and Slc39a5+/+ mice were placed on a NASH-inducing diet or NC for 40 wk and sacrificed after 16 hr of fasting. (A, B) NASH Slc39a5-/- mice display reduced serum ALT and AST levels. (C–E) Histology scores for steatosis, hepatocyte hypertrophy, and inflammation. (F) NAFLD activity score was reduced in NASH Slc39a5-/- mice. (G–I) NASH Slc39a5-/- mice display reduced fibrosis. (G) Representative images of explanted livers sample stained with picrosirius red indicative of collagen deposition. Scale bar, 300 µm. (H, I) Fibrosis and steatosis-activity-fibrosis scores. n=6–7 (NC) and 8–11 (NASH), *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test. Numeric data is summarized in Supplementary file 6.