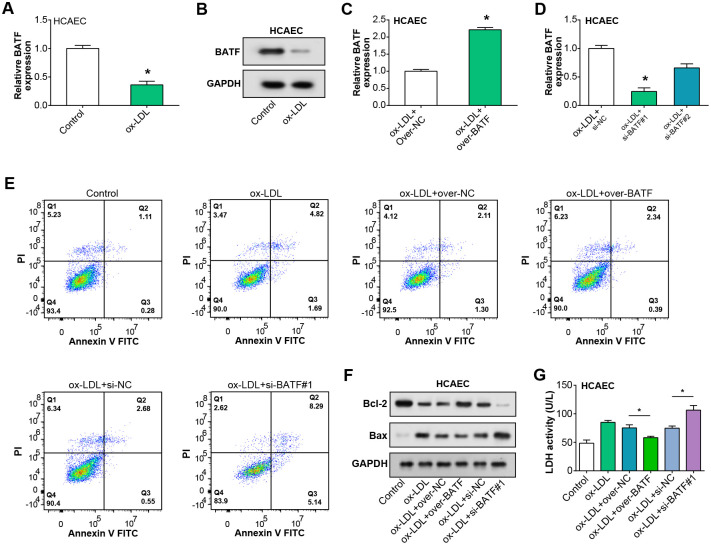
Fig 4. BATF alleviates the damage caused by ox-LDL induction in HCAEC.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of BATF mRNA expression in HCAEC cells following ox-LDL treatment. (B) WB analysis of BATF protein levels in HCAEC cells after ox-LDL treatment. (C) Efficiency of BATF overexpression in HCAEC cells post ox-LDL treatment, as assessed by qRT-PCR. (D) Efficiency of BATF knockdown in HCAEC cells post ox-LDL treatment, as determined by qRT-PCR. (E) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in HCAEC cells post ox-LDL treatment, with either BATF overexpression or knockdown. Quadrants represent different stages of cell death: Lower left, live cells; lower right, early apoptotic cells; upper right, late apoptotic cells; upper left, necrotic cells. (F) WB analysis of apoptosis-related proteins Bcl-2 and Bax in HCAEC cells after ox-LDL treatment and BATF overexpression or knockdown. (G) LDH activity in homogenates of HCAEC cells post ox-LDL treatment and either BATF overexpression or knockdown, as measured by the LDH assay kit. *p<0.05.