Abstract
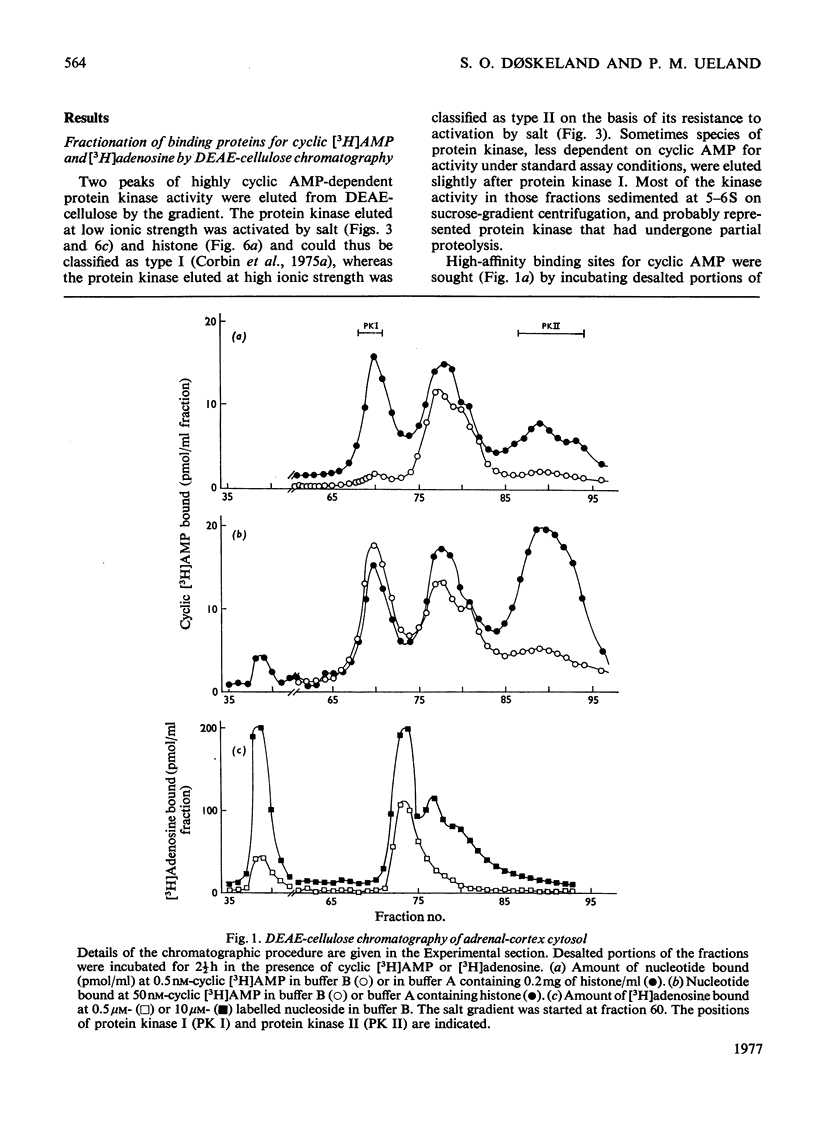
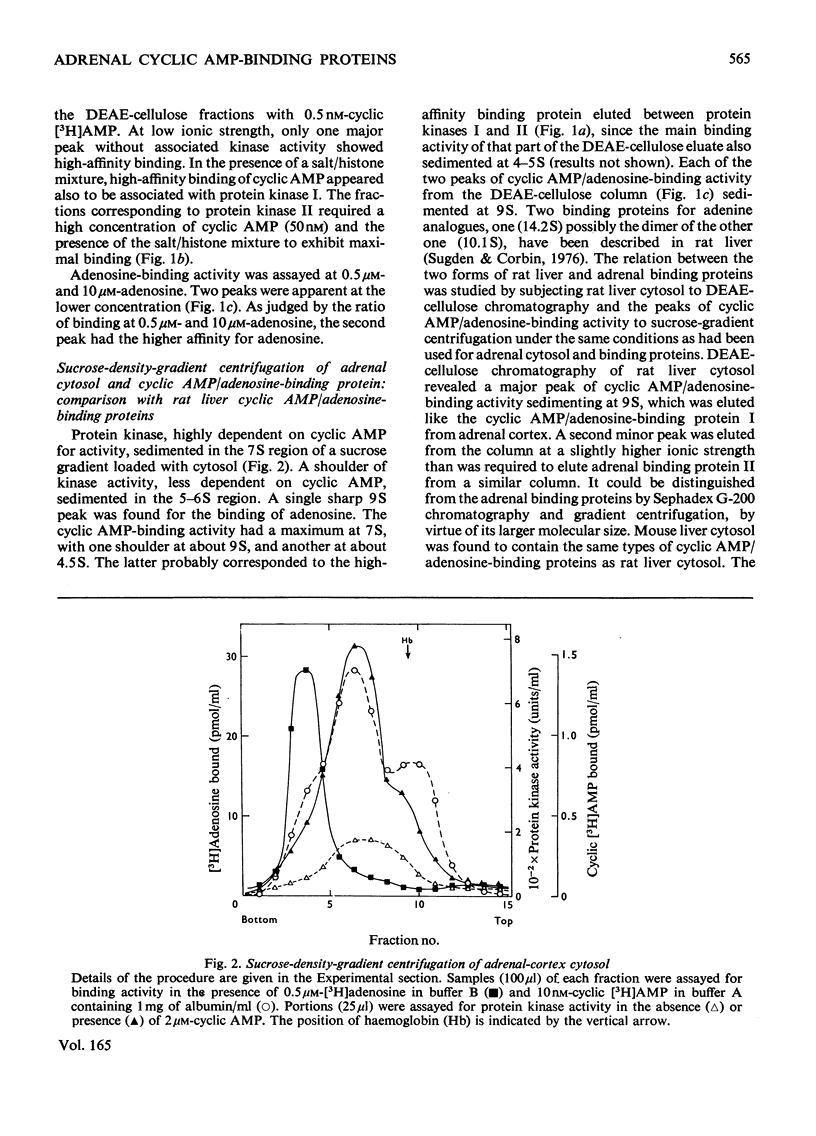
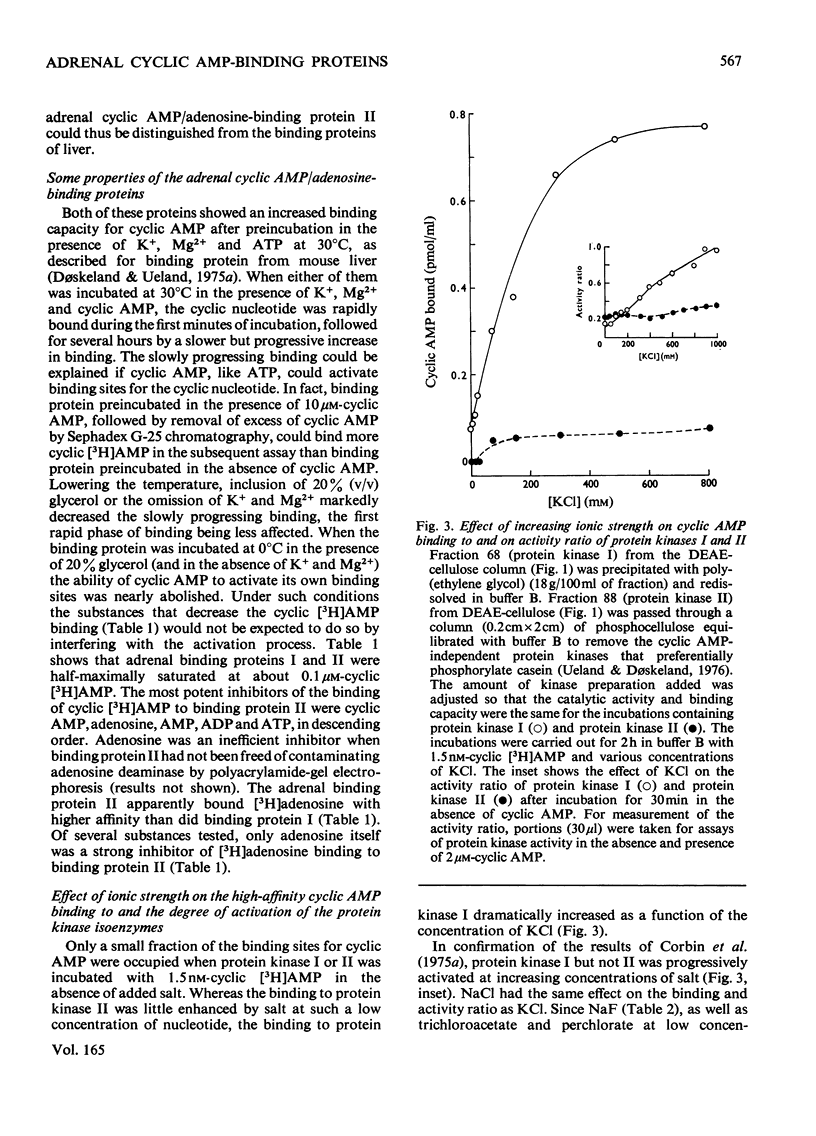
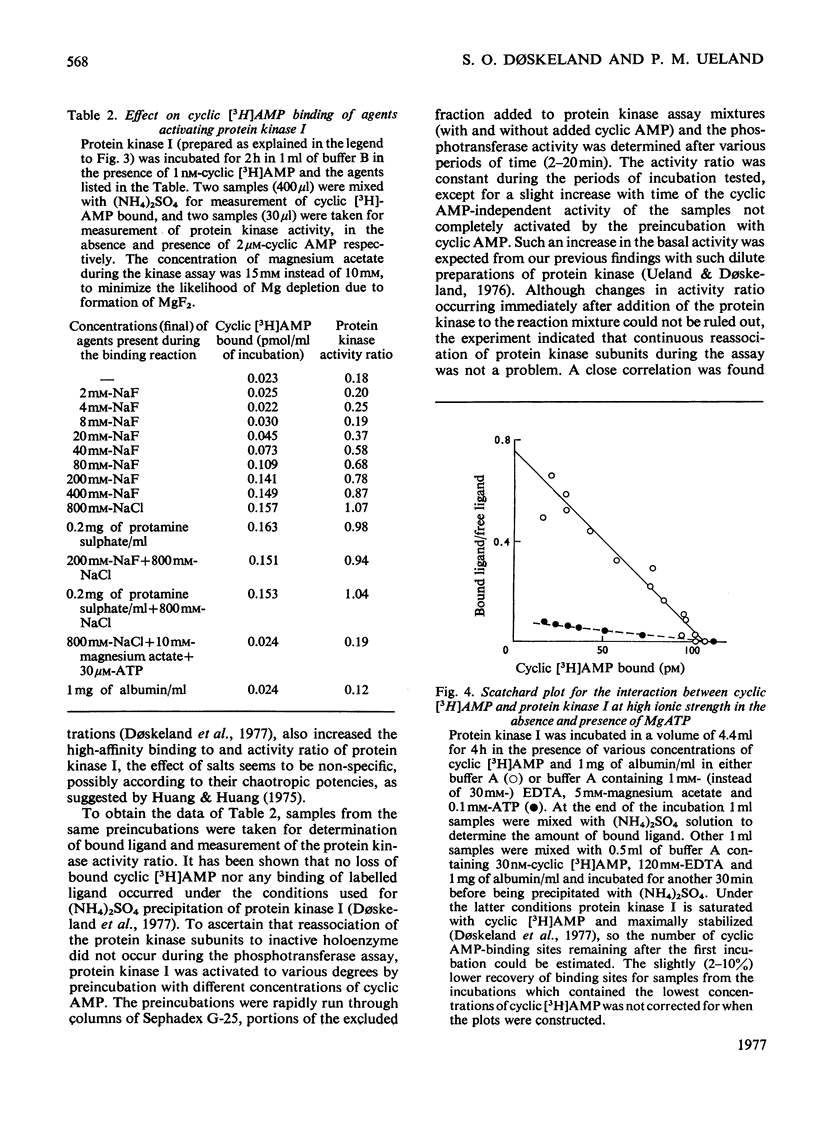
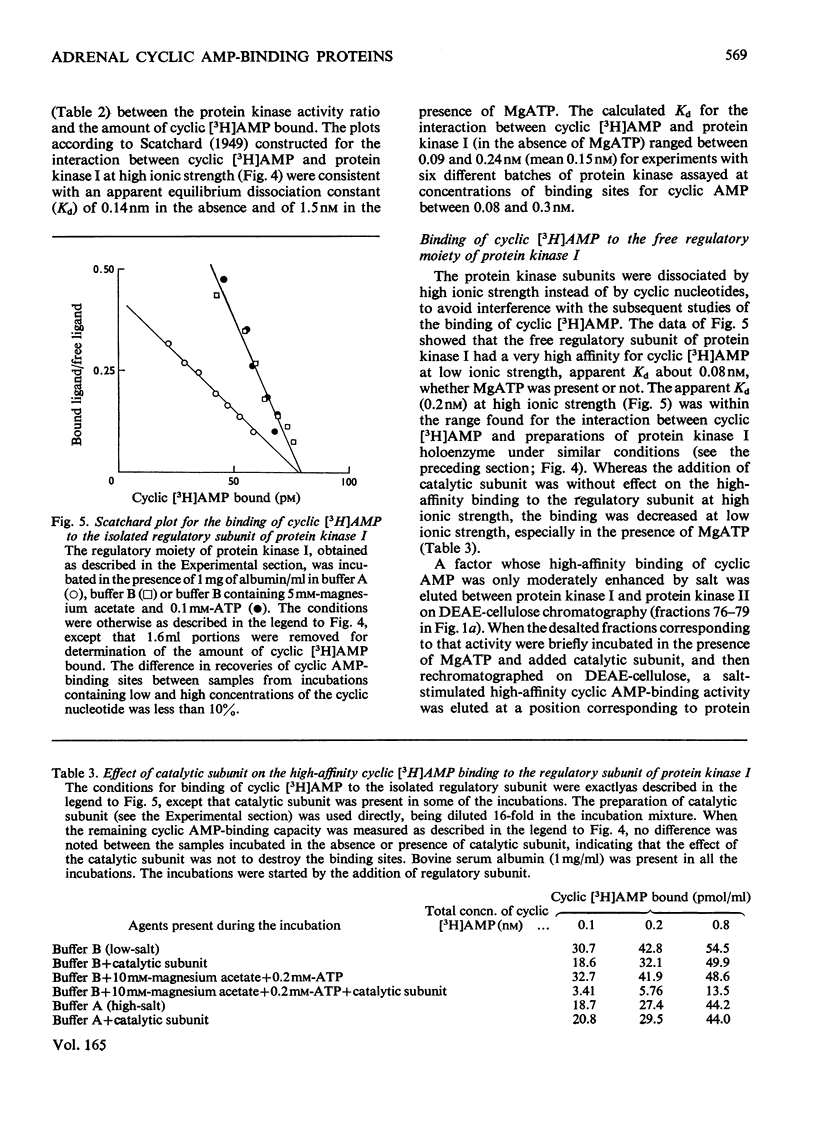
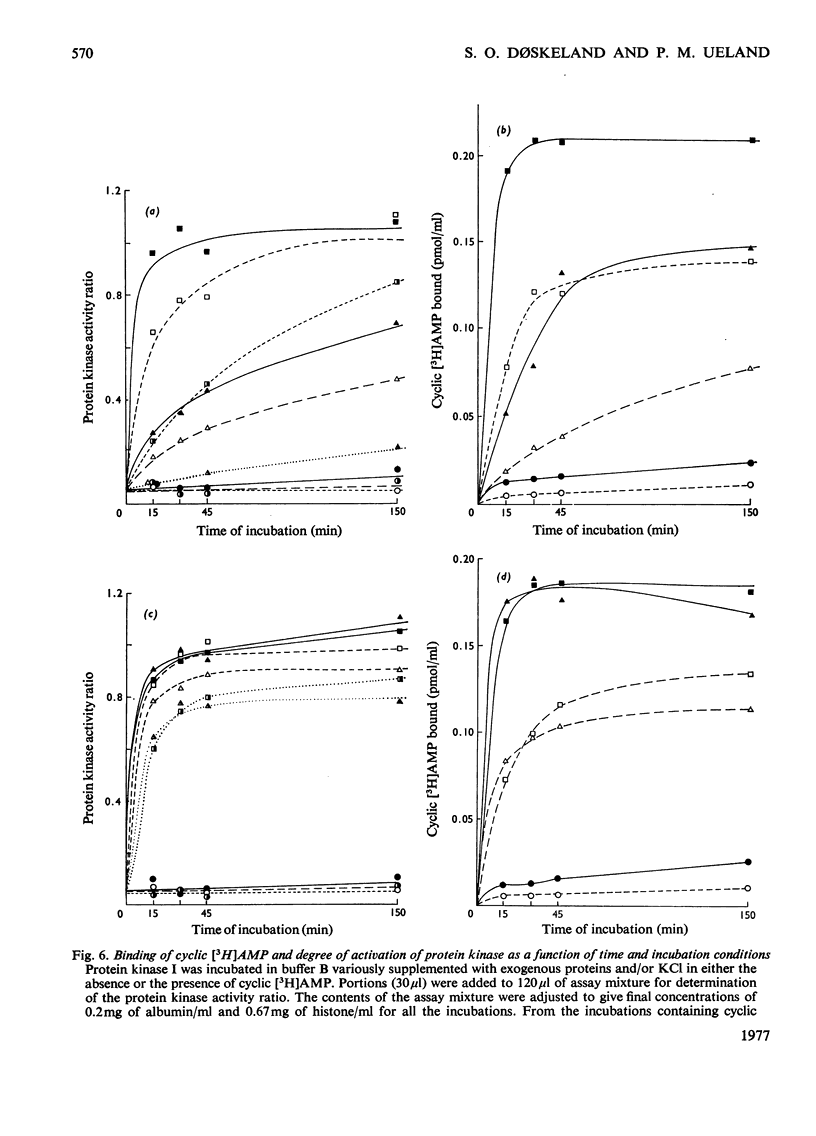
Five peaks of cyclic AMP-binding activity could be resolved by DEAE-cellulose chromatography of bovine adrenal-cortex cytosol. Two of the binding peaks co-chromatographed with the catalytic activities of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases (ATP–protein phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37) of type I or type II respectively. A third binding protein was eluted between the two kinases, and appeared to be the free regulatory moiety of protein kinase I. Two of the binding proteins for cyclic AMP, sedimenting at 9S in sucrose gradients, could also bind adenosine. They bound cyclic AMP with an apparent equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of about 0.1μm, and showed an increased binding capacity for cyclic AMP after preincubation in the presence of K+, Mg2+ and ATP. The two binding proteins differed in their apparent affinities for adenosine. The isolated regulatory moiety of protein kinase I had a very high affinity for cyclic AMP (Kd<0.1nm). At low ionic strength or in the presence of MgATP, the high-affinity binding of cyclic AMP to the regulatory subunit of protein kinase I was decreased by the catalytic subunit. At high ionic strength and in the absence of MgATP the high-affinity binding to the regulatory subunit was not affected by the presence of catalytic subunit. Under all experimental conditions tested, dissociation of protein kinase I was accompanied by an increased affinity for cyclic AMP. To gain some insight into the mechanism by which cyclic AMP activates protein kinase, the interaction between basic proteins, salt and the cyclic nucleotide in activating the kinase was studied.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Barnes G. D., Maudsley D. V., Brown B. L., Etkins R. P. Factors affecting the saturation assay of cyclic AMP in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):130–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke B. A., Lindh M. L., Janszen F. H. Correlation of protein kinase activation and testosterone production after stimulation of Leydig cells with luteinizing hormone. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1600439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Soderling T. R., Park C. R. Hormonal regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:265–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Ueland P. M. A cAMP receptor from mouse liver cytosol whose binding capacity is enhanced by Mg++-ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):606–613. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskeland S. O., Ueland P. M., Haga H. J. Factors affecting the binding of [3H]adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate to protein kinase from bovine adrenal cortex. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):653–665. doi: 10.1042/bj1610653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. A cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase from the adrenal cortex: comparison with a cyclic AMP binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. On the mechanism of action of adrenocorticotropic hormone: the binding of cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate to an adrenal cortical protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):512–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. Role of the receptor in the mechanism of action of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):786–790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Comparison of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rabbit skeletal and bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7795–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. C., Huang C. Rabbit skeletal muscle protein kinase. Conversion from cAMP dependent to independent form by chemical perturbations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):18–24. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klungsöyr L. Quantitative estimation of protein. Separation of alkaline protein-copper complex from excess copper on Sephadex G-25. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jan;27(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., MacDonald G. J., Garfink J. E. Role of histone kinases as mediators of corticotropin-induced steroidogenesis. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):1–9. doi: 10.1042/bj1600001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogez J. R., Segel I. H. Interaction of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate with protein kinase. Equilibrium binding models. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4551–4556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J., Rubin C. S. Molecular structure and characterization of bovine heart protein kinase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Corbin J. D. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-binding proteins in bovine and rat tissues. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):423–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1590423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Doskeland S. O. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependence of protein kinase isoenzymes from mouse liver. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):117–126. doi: 10.1042/bj1570117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Doskeland S. O. An adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-adenosine binding protein from mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):677–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh K. C., Tao M. Purification and characterization of adenosine-adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate binding protein factors from rabbit erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 3;13(25):5220–5226. doi: 10.1021/bi00722a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


