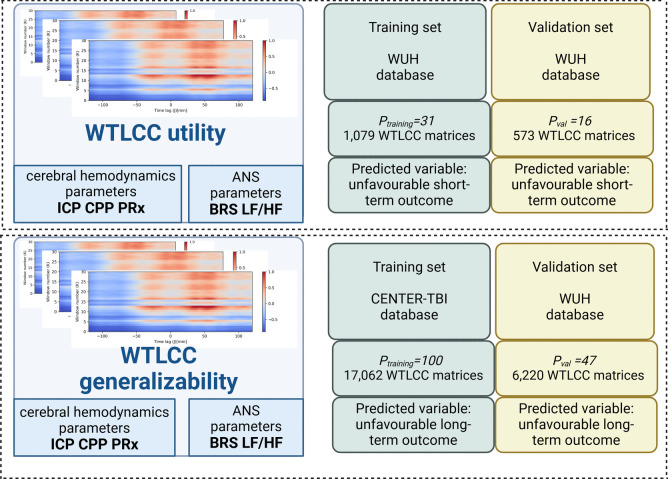
Fig. 1.
Study design. The aim of the first experiment (‘WTLCC utility’) was to investigate to the utility of windowed time-lag cross-correlation (WTLCC) matrices, which describe cerebral hemodynamics-autonomic nervous system (ANS) interactions for predicting short-term outcome. For cerebral hemodynamics parameters, intracranial pressure (ICP), cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP), pressure reactivity index (PRx) were used, and baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) and low-to-high component ratio of heart rate variability (LF/HF) were used as ANS metrics. This experiment was performed exclusively on the Wroclaw University Hospital (WUH) database. The second experiment (‘WTLCC generalizability’) aimed to evaluate the utility of WTLCC matrices for predicting long-term outcome in a larger, external database of TBI patients. For this purpose, the CENTER-TBI database was used for training, and the WUH database was used for validation