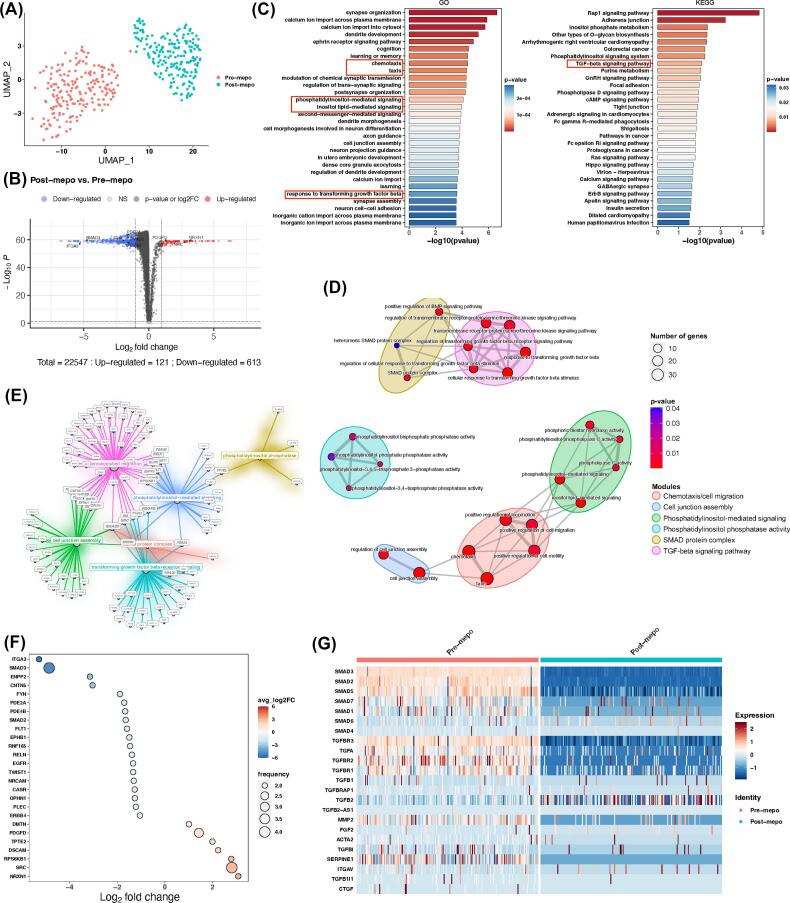
Fig. 4.
Effect of mepolizumab on the transcriptional profiles of eosinophils from patients with severe eosinophilic asthma detected by single-cell ribonucleic acid sequencing. (A) UMAP visualized the transcriptional distribution of pre- and post-mepo eosinophils. (B) Differential gene expression analysis in pre- and post-mepo eosinophils where genes were highlighted in blue (downregulated), gray (no change), black (no significant change), or red (upregulated). (C) Pathway enrichment analysis showing top list of pathways involved in the genes that are detected in the RNAseq. (D) Pathways with semantic similarity clustered into six functional modules. (E) Correlation of genes in the six functional modules. (F) Connecting node genes regulated by mepolizumab among the six functional modules. (G) Heatmap showing the comparison of expression levels of key genes involved in TGF-β pathway between pre- and post-mepo eosinophils. FC = fold change; GO = Gene ontology; KEGG = Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and Genomes; mepo = mepolizumab; RNAseq, ribonucleic acid sequencing; scRNAseq = single-cell ribonucleic acid sequencing; UMAP = Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection; TGF-β = transforming growth factor-β.