Figure 2. Inverted-U relationship between VNS actions and stimulation parameters.
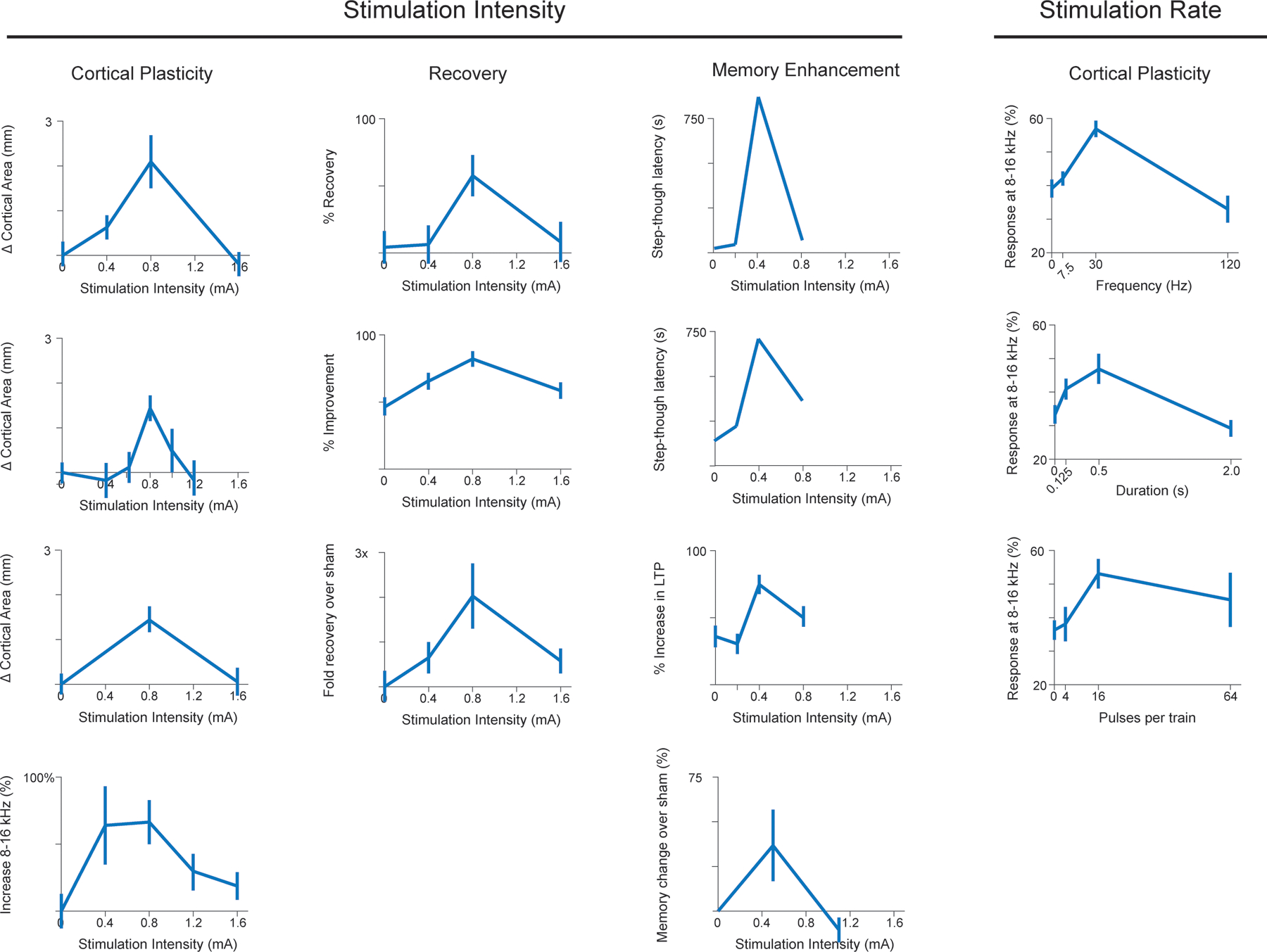
Across a wide range of models, applications, and measures, VNS effects exhibit an inverted-U relationship with the parameters of stimulation. Moderate stimulation intensity, frequency, and duration reliably produce the largest effects, whereas both lower and higher parameters are less effective. Data from, beginning in the top left and reading across, Morrison et al., Brain Stimulation, 2019; Pruitt et al., Translational Stroke Research, 2021; Clark et al., Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 1995; Buell et al., Brain Stimulation, 2018; Morrison et al, Behavioural Brain Research, 2020; Souza, Experimental Neurology, 2021; Clark et al., Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 1998; Buell et al., Neuroscience, 2019; Morrison et al., Brain Research, 2021; Unpublished; Zuo et al., Physiology & Behavior, 2007; Buell et al., Neuroscience, 2019; Borland et al., Brain Stimulation, 2016; Clark et al., Nature Neuroscience, 1999.
