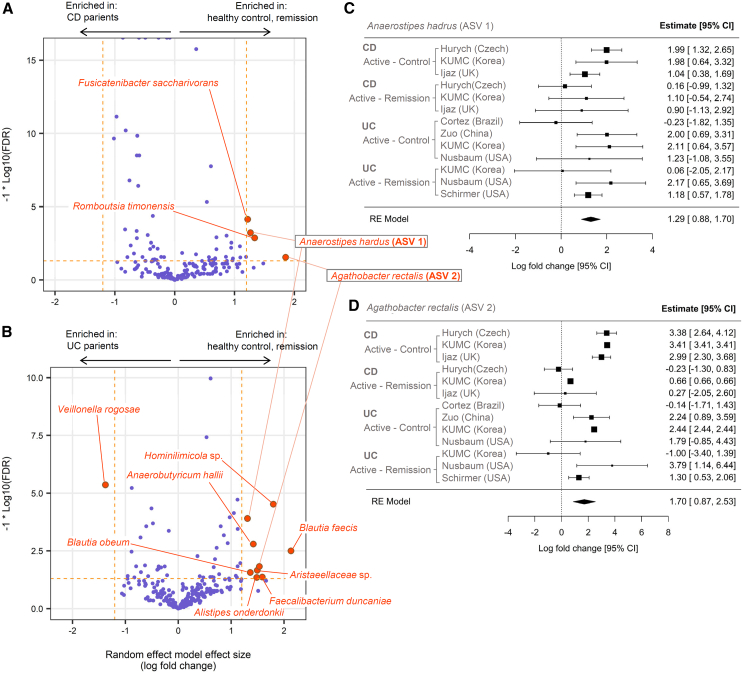
Figure 4.
Microbial markers of active CD and UC derived from meta-analysis of cohorts
(A) Effect size and false discovery rate (FDR) values of the ASVs estimated by random effect model combining ANCOM-BC results from three CD-HC comparisons and three CD-remission comparisons. The ASVs that pass the thresholds for FDR (<0.05) and effect size (absolute value of log fold change >1.2) are emphasized with larger point size and different color. Note that positive effect sizes mean higher abundance in either healthy control or remission state, depending on the analyzed dataset, compared to the active CD. Horizontal dashed line in orange corresponds to FDR value 0.05. Two vertical dashed lines in orange correspond to log fold change −1.2 and 1.2, respectively. Taxonomic names are displayed only for the ASVs that pass the FDR and log fold change thresholds.
(B) Same plot as (A) drawn for UC datasets.
(C and D) Forest plot representing meta-analysis summarization of the two selected ASVs. The square point and horizontal line range represent the estimated fold change and its 95% confidence interval, respectively. The ASV 1 (Anaerostipes hadrus) and ASV 2 (Agathobacter rectalis) were selected from (A) and (B) as these two were commonly detected as markers in both panels. The meta-analysis was performed with the rem function of the R package metafor, using the ANCOM-BC’s effect size and standard error values as inputs. See also Figures S1–S3 and Tables S3 and S4. ASVs, amplicon sequence variants; CD, Crohn disease; HC, healthy control; PIBD, pediatric inflammatory bowel disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.