Figure 2. Lipid resources for ferroptosis.
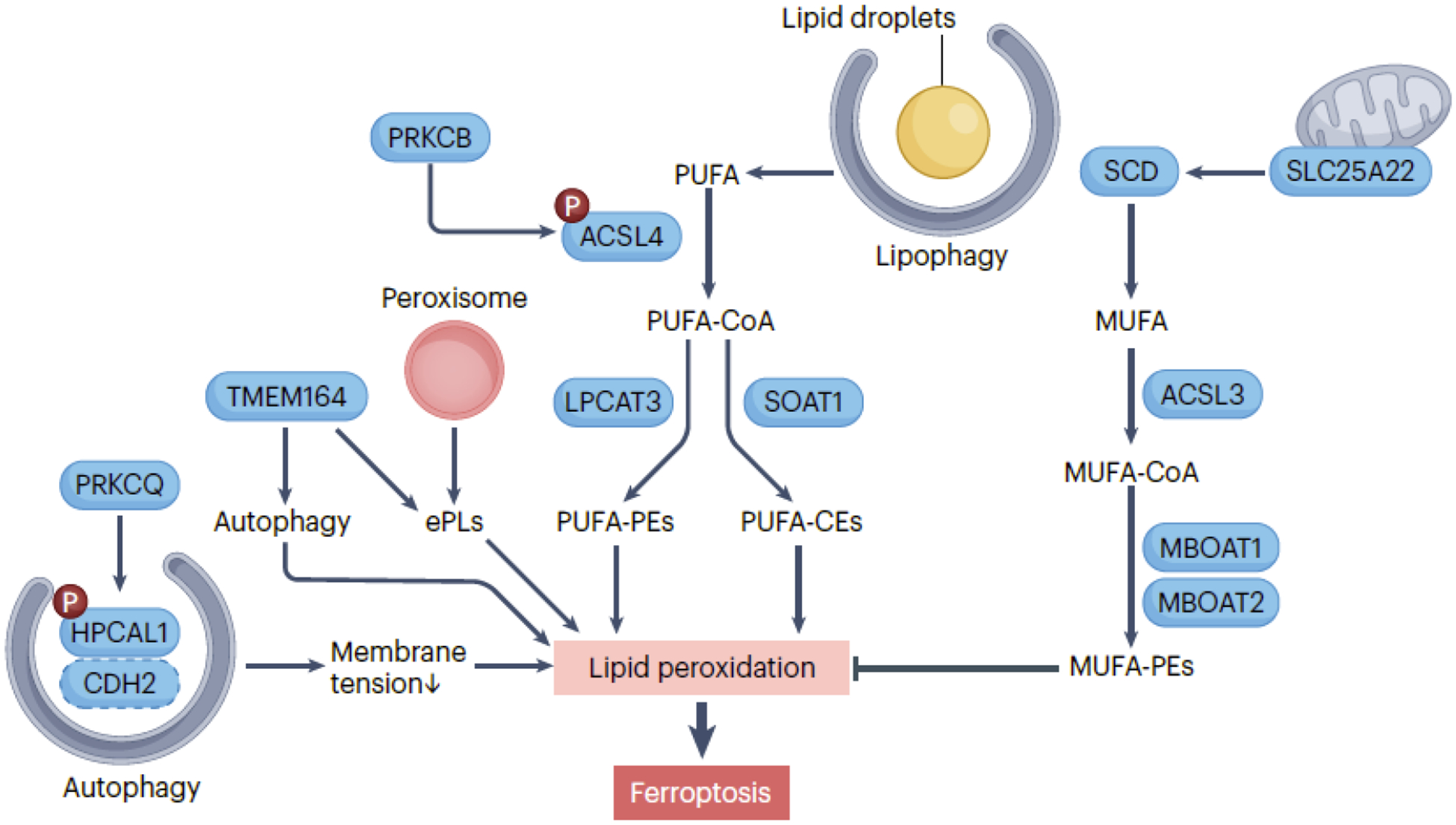
Cell membranes are the primary target of oxidative damage in ferroptosis, influenced by processes and metabolic pathways that promote lipid synthesis. ACSL4 (acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4) plays a critical role in activating polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) by converting them into acyl-CoA esters (PUFA-CoA), which serve as substrates for lipid peroxidation, contributing to the initiation of ferroptosis. Two downstream pathways involve LPCAT3 (lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3)-mediated PUFA-PEs and SOAT1 (sterol O-acyltransferase 1)-mediated PUFA-CEs. The activity of ACSL4 in ferroptosis is further enhanced by PRKCB (protein kinase C beta)-mediated ACSL4 phosphorylation. HPCAL1 (hippocalcin like 1) phosphorylation by PRKCQ (protein kinase C theta) promotes ferroptosis by inducing autophagic degradation of CDH2 (cadherin 2), leading to alterations in membrane tension in cancer cells. Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) synthesis mediated by SCD (stearoyl-CoA desaturase) and ACSL3 (acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 3) counteracts the initiation of ferroptosis by protecting against PUFA peroxidation. The mitochondrial transporter SLC25A22 (solute carrier family 25 member 22) plays a role in inhibiting ferroptosis by facilitating the production of SCD-mediated MUFA. MBOAT1 (membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 1) and MBOAT2 inhibit ferroptosis by remodeling the cellular phospholipid profile to produce MUFA-PEs. Peroxisomes contribute to the biosynthesis of ether phospholipids (ePLs), which are vulnerable to lipid peroxidation. TMEM164 (transmembrane protein 164) functions as an acyltransferase involved in ePLs synthesis or promotes the formation of autophagosomes. Lipophagy, the degradation of lipid droplets, releases lipids that can undergo peroxidation, increasing the susceptibility of cells to ferroptosis.
