Figure 3. Lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis.
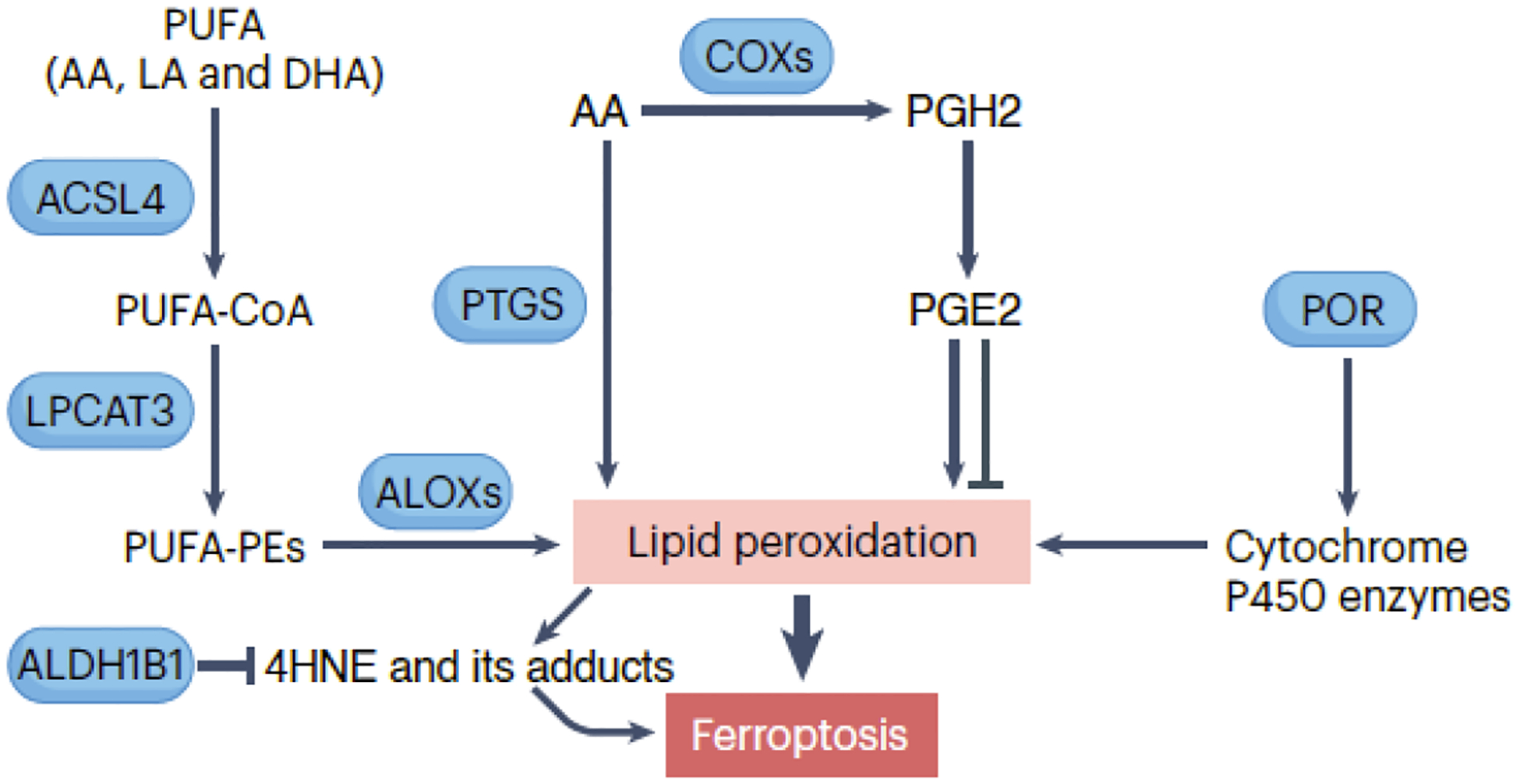
Several key enzymes participate in lipid peroxidation, including ALOX/lipoxygenase, PTGS/cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450 enzymes. ALOXs are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as arachidonic acid (AA), linoleic acid (LA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), leading to the formation of lipid hydroperoxides. PTGS/cyclooxygenase enzymes are involved in prostaglandin synthesis but can also catalyze lipid peroxidation. The production of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) and subsequently prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) promotes or inhibits ferroptosis in a context-dependent manner. Additionally, POR plays a role by supplying electrons to cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the production of lipid hydroperoxides. These hydroperoxides can undergo further reactions, such as decomposition and rearrangement, generating highly reactive lipid radicals. Ultimately, this cascade of reactions can disrupt membrane integrity and contribute to ferroptotic cell death.
