Figure 4. Enzymatic antioxidants in ferroptosis.
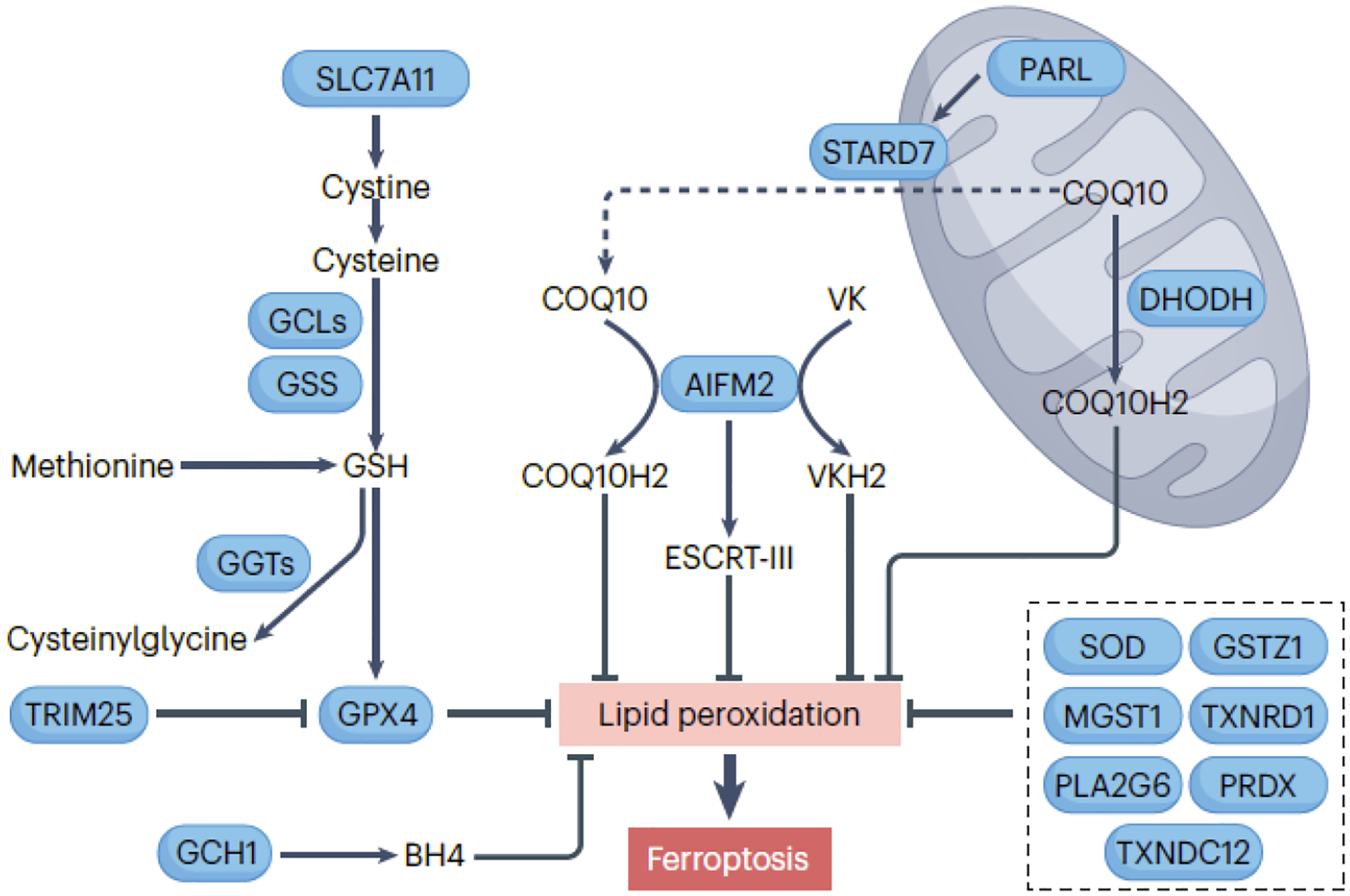
The main enzyme central to the antioxidant defense against ferroptosis is GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4), which requires the tripeptide cofactor glutathione (GSH), composed of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. SLC7A11 (solute carrier family 7 member 11) is a key component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc−, responsible for allowing the uptake of cystine, which is then reduced to cysteine within the cells. The synthesis of the majority of cellular GSH involves the rate-limiting substrate cysteine, catalyzed by GCLC (glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit) and GSS (glutathione synthetase). Cysteine can also be derived from the metabolism of methionine. A family of enzymes called GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) catalyze the breakdown of GSH into cysteinylglycine and free amino acids. AIFM2 (apoptosis inducing factor mitochondria associated 2) and DHODH dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone)) play pivotal roles in the reduction of COQ10 (coenzyme Q10) to its antioxidant form, COQ10H2, in the plasma membrane/cytoplasm and mitochondria, respectively. The cleavage of STARD7 (StAR related lipid transfer domain containing 7) by the rhomboid protease PARL (presenilin associated rhomboid like) is essential for the synthesis and transport of COQ10 to the plasma membrane/cytoplasm, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis. Furthermore, AIFM2-mediated membrane repair and vitamin K (VK) reduction also contribute to its antiferroptotic activity. GCH1 (GTP cyclohydrolase 1) participates in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a cofactor that helps maintain cellular redox balance and antioxidant defenses, thereby inhibiting susceptibility to ferroptotic cell death. Several other enzymes, such as SOD2 (superoxide dismutase) family, MGST1 (microsomal glutathione S-transferase 1), GSTZ1 (glutathione S-transferase zeta 1), TXNRD1 (thioredoxin reductase 1), PLA2G6 (phospholipase A2 group VI), and PRDX (peroxiredoxin) family inhibit ferroptosis in some cases.
