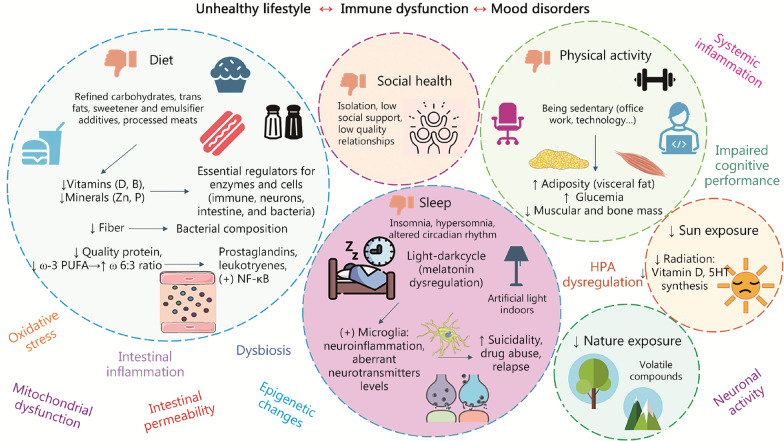
Fig. 5.
The relationship between lifestyle, immune dysfunction, and mood disorders. As summarized, diet, social health, physical activity, sleep, nature and sun exposure are major modulators of the immune system and other relevant factors associated. As explained, it is common that patients with mood disorders present unhealthy dietary patterns, with increased intake of certain components like refined carbohydrates and reduced micronutrients; sleep problems like insomnia, hypersomnia, or altered circadian rhythms; a poor quality of social relationships and isolation; reduced levels of physical activity and sedentarism and also; insufficient sun and nature exposure, missing the opportunity to positively regulate their immune system. Zn zinc, P phosphorus, ꞷ-6:3 ratio omega-6:3, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio, HPA hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa B, 5HT serotonin