Fig. 1.
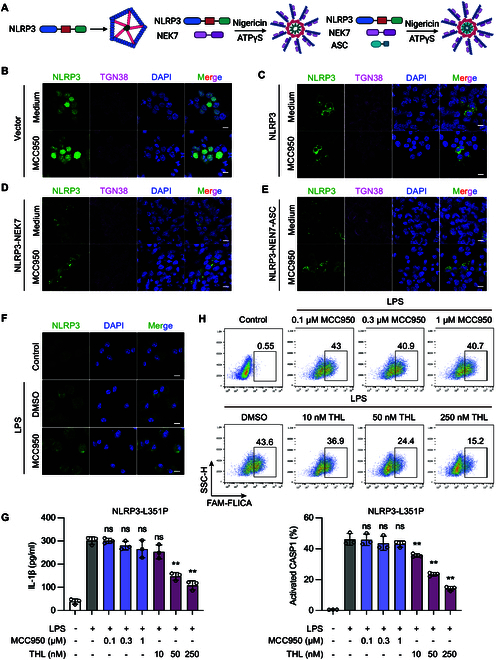
The activation form NLRP3 inflammasome complex shows resistance to MCC950. (A) Cage-NLRP3, NLRP3-NEK7, and NLRP3-NEK7-ASC complexes were re-constituted in HEK293T cells. For cage-NLRP3, HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP-NLRP3 only; for the NLRP3-NEK7 complex, HEK293T cells cotransfected with GFP-NLRP3 and HA-NEK7 were stimulated with nigericin, and then ATPγS and MgCl2 were added to lock NLRP3 in an active conformation. For NLRP3-NEK7-ASC complex, HEK293T cells cotransfected with GFP-NLRP3, HA-NEK7, and ASCPYD were stimulated with nigericin, and then ATPγS and MgCl2 were added. (B) GFP-tagged vector (C) Cage-NLRP3, (D) NLRP3-NEK7, and (E) NLRP3-NEK7-ASC complexes were reproduced in HEK293T cells. The effect of MCC950 on 3 stages of NLRP3 complexes was observed by confocal microscopy. (F) BMDMs stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS were treated with 1 μM MCC950 for 1 h. NLRP3 oligomer formation was examined using IF. (G and H) NLRP3lyz−/− BMDMs were recombined with mouse NLRP3 L351P mutant (L351P-BMDM). L351P-BMDMs were treated with indicated concentrations of MCC950 or THL followed by 100 ng/ml LPS for 3 h. (G) IL-1β in the supernatant was determined by ELISA. (H) CASP1 activation was determined by FAM-FLICA staining. Scale bar, 10 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
