Fig. 3.
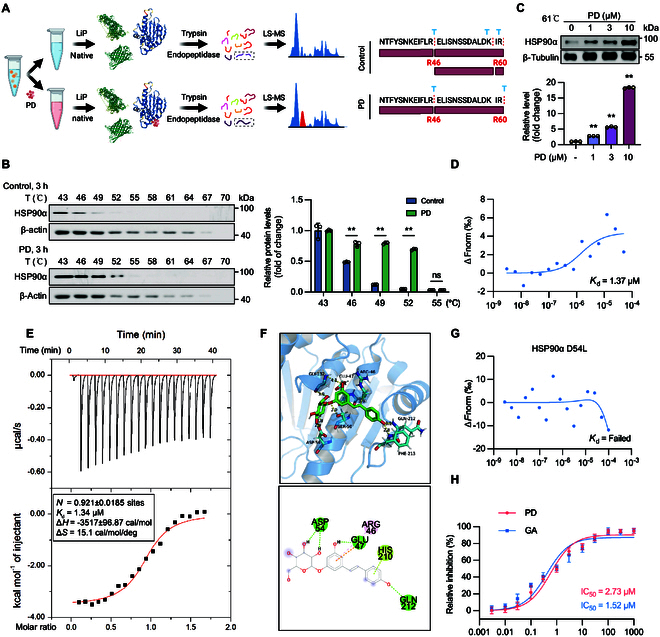
Polydatin directly binds to HSP90α. (A) Schematic representation of systematic identification of protein–small molecule interactions using Lip-SMap. (B) BMDMs were incubated with polydatin (DMSO as control) for 3 h, cells were collected, and CETSA was performed. (C) BMDMs were incubated with indicated concentrations of polydatin for 3 h, cells were collected, and CETSA was performed at 61 °C. (D) The affinity between polydatin and recombinant HSP90α protein was assessed by MST assay. (E) ITC enthalpogram of the interaction between polydatin and HSP90α at 25 °C. The titration curve shows the relationship between the molar ratio of HSP90α to the calculated concentration of polydatin in the assay. (F) Binding poses of polydatin against HSP90α (Protein Data Bank ID: 5H22). (G) The affinity between polydatin and recombinant HSP90α D54L mutant protein was assessed by MST assay. (H) Effect of polydatin and GA on the ATPase activity of HSP90α. After incubation of HSP90α with indicated different concentrations of polydatin or GA, ATPase was measured by Ultra-trace total ATPase test kit. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
