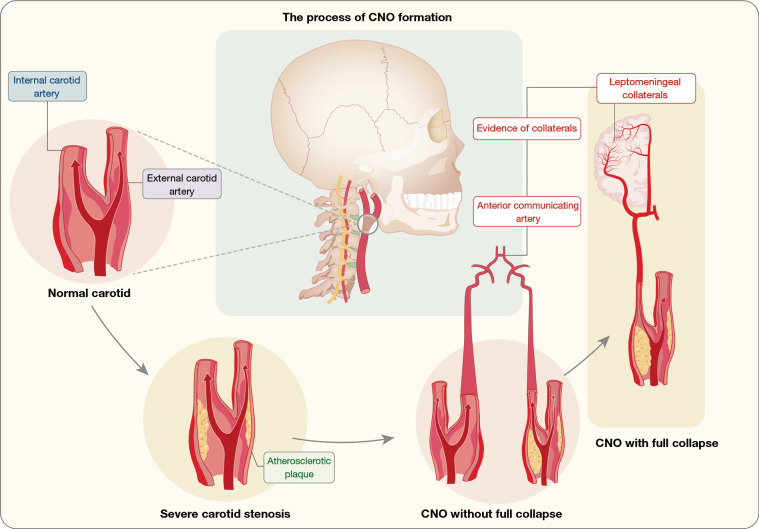
Figure 1.
The transformation of a normal ICA into a CNO with full collapse. Initially, the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques in normal carotid arteries leads to lumen stenosis, while the distal lumen diameter of ICA remains normal. However, as stenosis progresses, the lumen diameter of the distal ICA diminishes, becoming smaller than that of the contralateral ICA and the ipsilateral ECA. At this stage, ordinary stenosis evolves into a CNO without full collapse and is accompanied by the opening of the intracranial branch circulation. Once the distal diameter completely collapses and assumes a “linear” configuration, a type of CNO with full collapse is formed. CNO, carotid near occlusion; ICA, internal carotid artery; ECA, external carotid artery.