Abstract
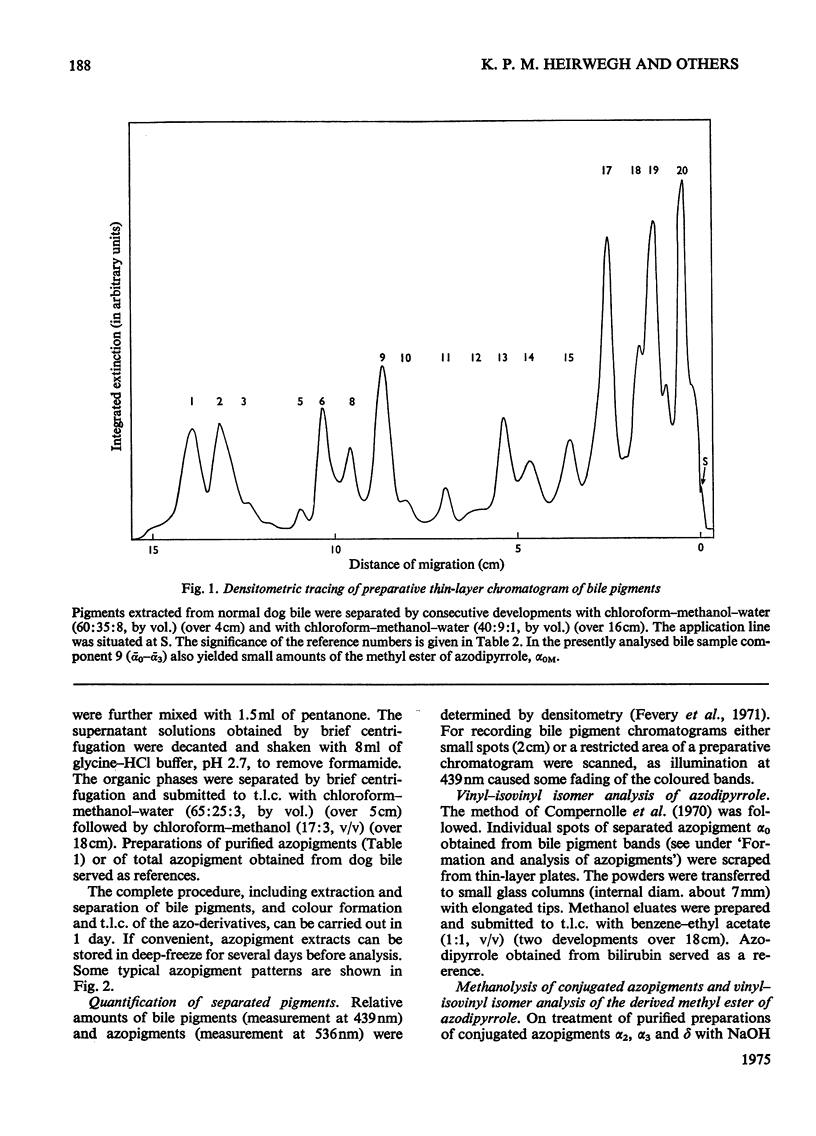
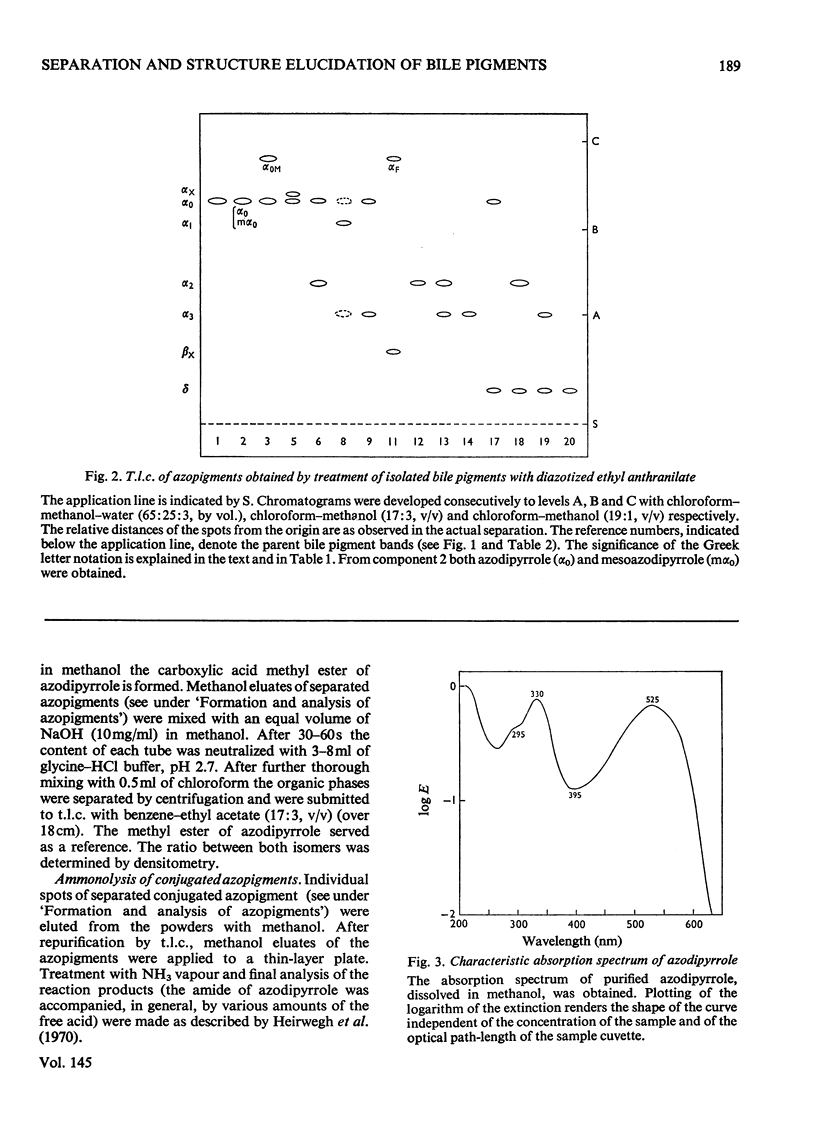
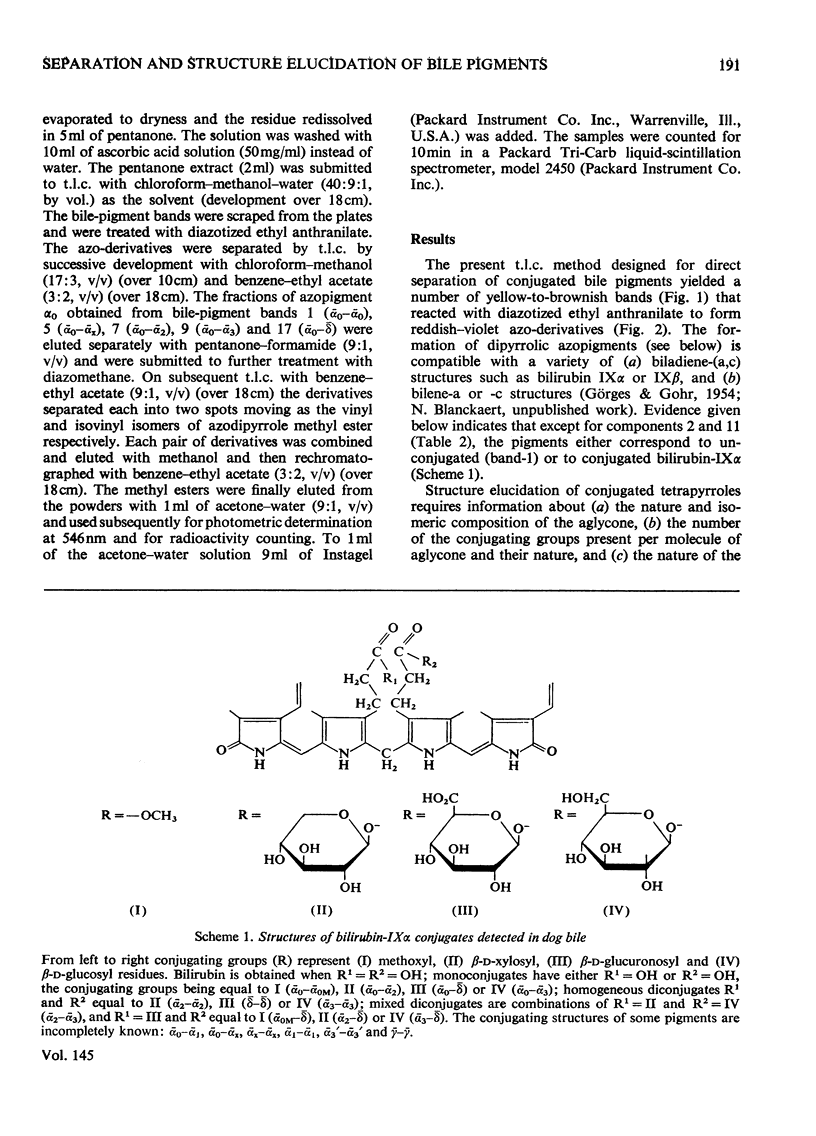
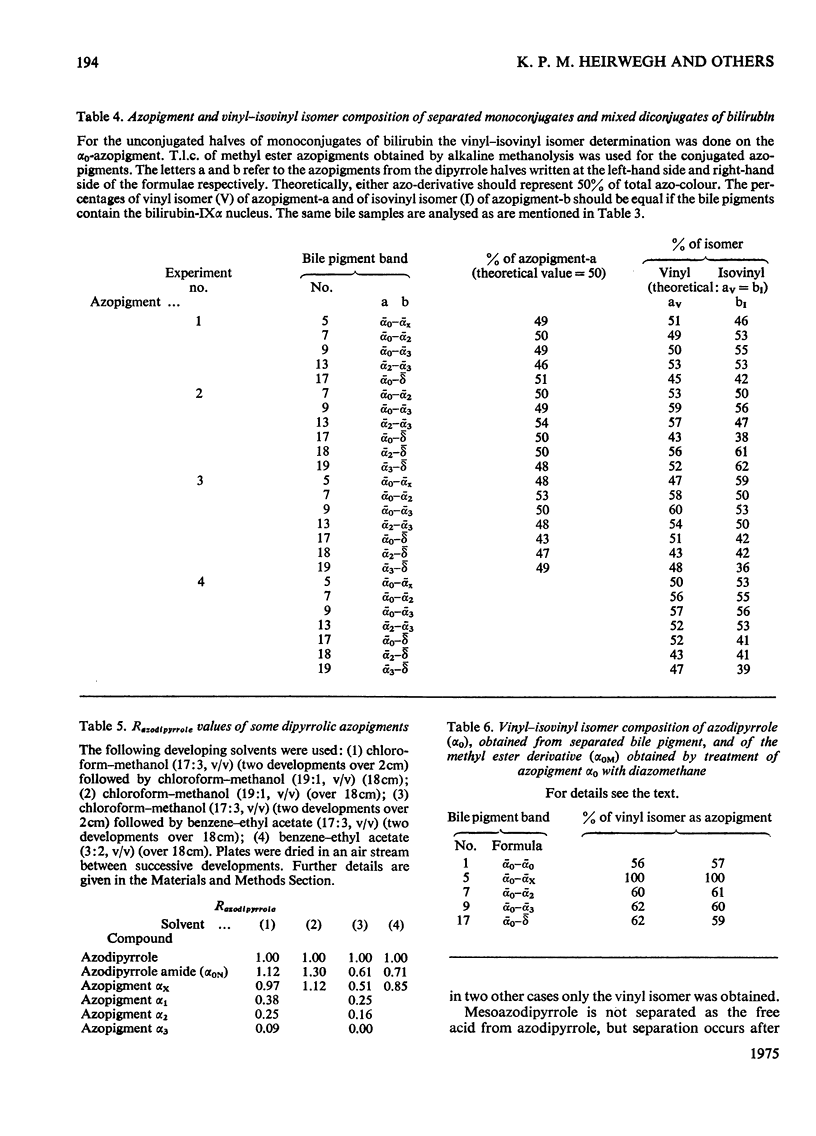
1. A system for separation of bile pigments by t.l.c. and for their structure elucidation is presented. Separated bile pigments are characterized by t.l.c. of derived dipyrrolic azopigments. 2. At the tetrapyrrolic stage hydrolysis in strongly alkaline medium followed by t.l.c. demonstrates the presence of bilirubin-IIIalpha, -IXalpha and -XIIIalpha and allows assessment of their relative amounts. 3. Most structural information is derived from analysis of dipyrrolic azopigments. Such derivatives, obtained by treatment of separated bile pigments with diazotized ethyl anthranilate, were separated and purified by t.l.c. Micro methods showed (a) the nature of the dipyrrolic aglycone, (b) the nature of the bonds connecting aglycone to a conjugating group, (c) the ratio of vinyl/isovinyl isomers present in the aglycone and, (d) the nature of the conjugating groups (by suitable derivative formation and t.l.c. with reference to known compounds). 4. In bile of normal dogs at least 20 tetrapyrrolic, diazo-positive bile pigments could be recognized. Except for two pigments the tetrapyrrolic nucleus corresponded predominantly to bilirubin-IXalpha. All conjugated pigments had their conjugating groups connected in ester linkage to the tetrapyrrolic aglycone, Apart from bilirubin-IXalpha, monoconjugates and homogeneous and mixed diconjugates of bilirubin were demonstrated; conjugating groups of major importance were xylose, glucose and glucuronic acid. 5. Bilirubin isomer determination on native bile and isolated bile pigments, and dipyrrole-exchange assays with [14C8]bilirubin indicated (a) that the conjugates pre-exist in bile, and (b) that no significant dipyrrole exchange occurs during isolation of the pigments.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILLING B. H., COLE P. G., LATHE G. H. The excretion of bilirubin as a diglucuronide giving the direct van den Bergh reaction. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):774–784. doi: 10.1042/bj0650774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Fevery J., Parker D., Jacobson J., Billing B. H., Carson E. R. Effect of phenobarbitone on plasma (14C)bilirubin clearance in patients with unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jan;46(1):1–17. doi: 10.1042/cs0460001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN B. J. A modified bile return system in the dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:122–124. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE P. G., LATHE G. H., BILLING B. H. Separation of the bile pigments of serum, bile and urine. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):514–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0570514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compernolle F., Jansen F. H., Heirwegh K. P. Mass-spectrometric study of the azopigments obtained from bile pigments with diazotized ethyl anthranilate. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):891–894. doi: 10.1042/bj1200891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compernolle F., Van Hees G. P., Fevery J., Heirwegh K. P. Mass-spectrometric structure elucidation of dog bile azopigments as the acyl glycosides of glucopyranose and xylopyranose. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):811–819. doi: 10.1042/bj1250811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Leroy P., Van de Vijver M., Heirwegh K. P. Structures of bilirubin conjugates synthesized in vitro from bilirubin and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, uridine diphosphate glucose or uridine diphosphate xylose by preparations from rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):635–644. doi: 10.1042/bj1290635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Van Damme B., Michiels R., De Groote J., Heirwegh K. P. Bilirubin conjugates in bile of man and rat in the normal state and in liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2482–2492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Van Hees G. P., Leroy P., Compernolle F., Heirwegh K. P. Excretion in dog bile of glucose and xylose conjugates of bilirubin. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):803–810. doi: 10.1042/bj1250803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORGES T., GOHR H. Untersuchungen über das Vorkommen von Dihydromesobilirubin in den Faeces beim Menschen. Dtsch Z Verdau Stoffwechselkr. 1954 Aug;14(4):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. R., Dadoun M., Goresky C. A., Chan T. H., Perlin A. S. The isolation of an azobilirubin beta-D-monoglucoside from dog gall-bladder bile. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):97–105. doi: 10.1042/bj1430097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heirwegh K. P., Fevery J., Meuwissen J. A., De Groote J., Compernolle F., Desmet V., Van Roy F. P. Recent advances in the separation and analysis of diazo-positive bile pigments. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:205–250. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heirwegh K. P., Meuwissen J. A., Fevery J. Critique of the assay and significance of bilirubin conjugation. Adv Clin Chem. 1973;16:239–288. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heirwegh K. P., Van Hees G. P., Leroy P., Van Roy F. P., Jansen F. H. Heterogeneity of bile pigment conjugates as revealed by chromatography of their ethyl anthranilate azopigments. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):877–890. doi: 10.1042/bj1200877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen F. H., Billing B. H. The identification of monoconjugates of bilirubin in bile as amide derivatives. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):917–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1250917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen F. H., Stoll M. S. Separation and structural analysis of vinyl- and isovinyl-azobilirubin derivatives. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):585–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1250585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L. Mono- and diglucuronidation of bilirubin. Folia Med Neerl. 1972;15(4):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L. The isomerisation of bilirubin monoglucuronide. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Dec 12;49(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C. Bilirubin conjugates of human bile. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance, infrared and optical spectra of model compounds. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):395–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1190395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C. Bilirubin conjugates of human bile. The excretion of bilirubin as the acyl glycosides of aldobiouronic acid, pseudoaldobiouronic acid and hexuronosylhexuronic acid, with a branched-chain hexuronic acid as one of the components of the hexuronosylhexuronide. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):411–435. doi: 10.1042/bj1190411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe G. H. The degradation of haem by mammals and its excretion as conjugated bilirubin. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:107–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. Commercial bilirubin: A trinity of isomers. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80475-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. The ready isomerization of bilirubin IX- in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1290797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol A. W., Morell D. B. Studies on the isomeric composition of biliverdin and bilirubin by mass spectrometry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Colleran E. Separation and identification of biliverdin isomers and isomer analysis of phycobilins and bilirubin. J Chromatogr. 1970 Aug 12;50(3):458–468. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTROW J. D., HAMMAKER L., SCHMID R. The preparation of crystalline bilirubin-C14. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1442–1452. doi: 10.1172/JCI104375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. D., Murphy N. H. Isolation and properties of conjugated bilirubin from bile. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):311–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1200311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryka Z. J. Identification of isomers differing from 9, alpha, in the early labelled bilirubin of the bile. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):464–466. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R. The identification of direct-reacting bilirubin as bilirubin glucuronide. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Gray C. H. The oxidation products of crude mesobilirubinogen. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):271–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1170271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALAFANT E. Properties and composition of the bile pigment giving a direct diazo reaction. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):312–312. doi: 10.1038/178312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton G., Gray C. H. Gas chromatographic analysis of pyrrolic acid esters from the potassium permanganate oxidation of bile pigments. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):29–43. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


