Fig. 3.
Development of antigen-specific mAbs from single B cells
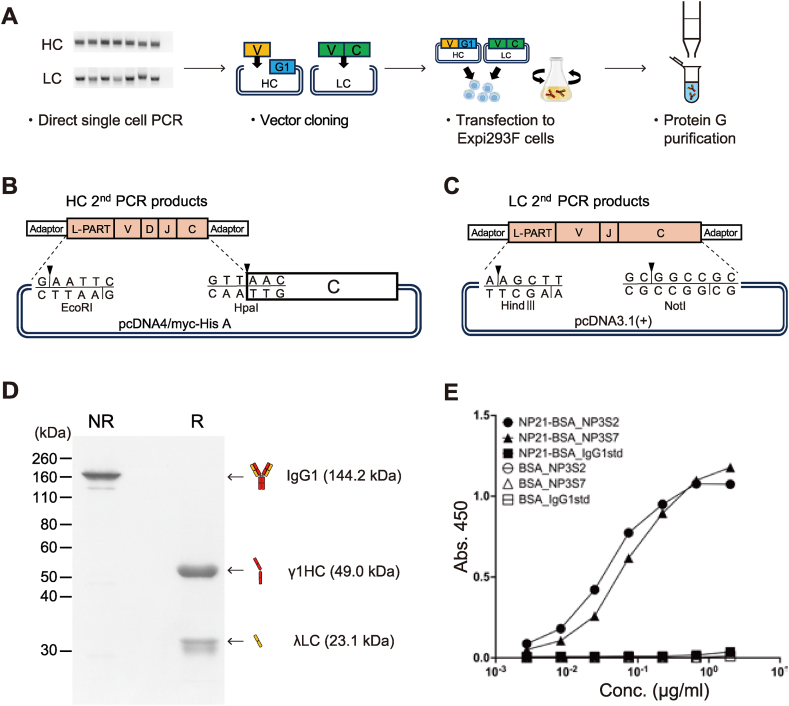
(A) Schematic workflow of mAb purification from single memory B cells. Step 1: HC and LC gene amplification by RT-PCR. Step 2: PCR products were cloned into expression vectors. Step 3: HC and LC expression plasmids were co-transfected into Expi293F cells. Step 4: mAbs were purified from culture supernatant by Protein G affinity purification.
(B) Cloning of variable domain into IgG1 HC expression vector containing IgG1 CH1 (from 41Asn) to CHS domain.
(C) Cloning of full-length LC gene into the expression vector.
(D) γ1HC and λLC expression plasmids encoding NP3S2 IgG1 were transfected into Expi293F cells. 3 μg of purified NP3S2 IgG1 antibody per well was separated on 10 % SDS-PAGE either non-reducing (NR) or reducing (R) conditions.
(E) mAbs NP3S2 and NP3S7 were produced in a combination of HC with paired LC obtained from single cells. NP3S2 and NP3S7 correspond to #2 and #7 in Fig. 2D. The NP-binding activity was measured by ELISA against NP21-BSA or BSA. IgG1std, mouse IgG1 standard.