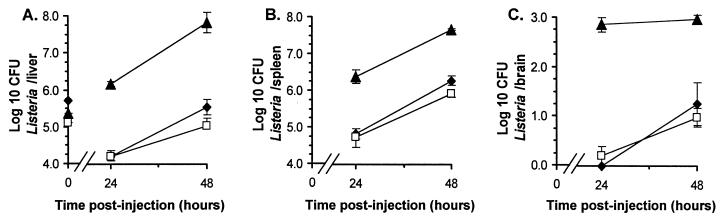
FIG. 5.
Intraperitonal injection of infected cells leads to bacterial dissemination. J774A.1 cells were infected by 2-h incubation with L. monocytogenes, and peritoneal cells were harvested by peritoneal lavage from mice 60 min following i.p. injection with 107 L. monocytogenes organisms. Infected J774A.1 cells (▴; 5.37 log10 CFU) and peritoneal cells (⧫; 5.72 log10 CFU) or broth-grown bacteria (□; 5.11 log10 CFU) were injected i.p. into mice, and CFU of bacteria in liver (A), spleen (B), and brain (C) were quantified 24 and 48 h postinjection. CFU of bacteria in each inoculum (log10 per mouse) are shown with the symbols described above at time zero in panel A. Results shown are the mean log10 CFU of bacteria/organ ± SEM from groups of four mice. Error bars not shown are smaller than the symbol.