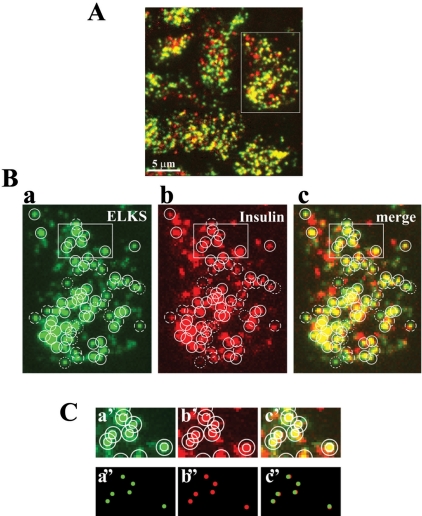
Figure 4.
Colocalization of ELKS clusters and insulin granules in the plasma membrane of MIN6 cells analyzed by TIRFM. (A) Cells were fixed and double immunostained using anti-ELKS pAb, anti-insulin mAb, and secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor-488–conjugated anti-rabbit and Alexa Fluor-546–conjugated anti-mouse antibodies). The colocalization of ELKS clusters (green) and insulin granules (red) is demonstrated by the overlap (yellow) of green and red channel images. (B) Most ELKS clusters (a, green) corresponded to sites of docked insulin granules (b, red). Box in the abovementioned image indicates the region that is magnified below. Each circle (1 μm in diameter) in the green channel corresponds to the circle in the red channel. Solid circles represent the colocalization of ELKS clusters and insulin granules (positive). Dotted circles indicate observed ELKS clusters but not insulin granules (negative). Dashed circles indicate ELKS clusters with only a partially corresponding overlap (neutral). (C) Boxes in the above-mentioned images indicate regions that are magnified below. Inner circles (400 nm in diameter) were drawn around fluorescent spots in each image (a′, b′, and c′). Sizes of circles in images (a′) and (b′) were reduced to 64% (257 nm in diameter) and 68% (270 nm in diameter), respectively, to correct to the real diameters (a″ and b″), and these were transferred to identical pixel localizations (c″). Circles of ELKS clusters (green) and insulin granules (red) overlapped (rated as positive).