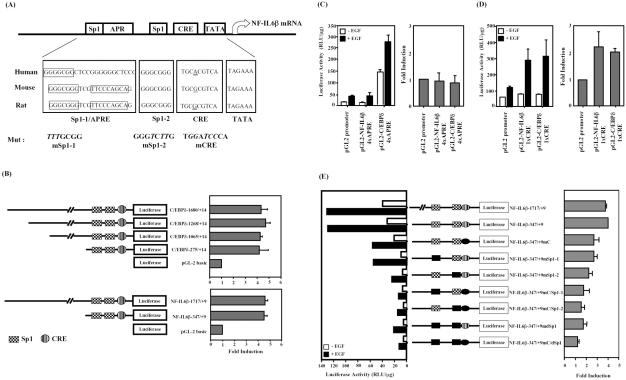
Figure 2.
Mapping of promoter elements required for EGF activation of the NF-IL6β reporter gene. (A) Putative conserved sites alignment of promoter sequences of human, mouse and rat C/EBPδ genes. The consensus sequences of the Sp1/APRE, CRE, and TATA sites are blocked. The mutated sequence in each individual construct is shown in italics and bold. (B) Activation of the C/EBPδ and NF-IL6β promoter by EGF in A431 cells. A431 cells transfected with various luciferase reporters as indicated were stimulated with or without EGF. The average fold inductions by EGF for each construct are shown. The minimal EGF responsive regions of C/EBPδ and NF-IL6β gene were represented by bold. (C and D) Characterization of heterologous reporters containing APRE or CRE elements contributed to EGF response. The heterologous reporters were transiently transfected to A431 cells and treated with or without EGF for 15 h. (E) Functional roles of binding sites for Sp1- or CREB-related transcriptional factors in the NF-IL6β promoter activity. A431 cells transfected with various luciferase reporters as indicated were stimulated with or without EGF, and the lysates were analyzed for luciferase activity (left). Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments, and the data shown here were from one representative assay. The average fold induction (mean ± SD, n = 3) by EGF for each construct was analyzed (right).