Abstract
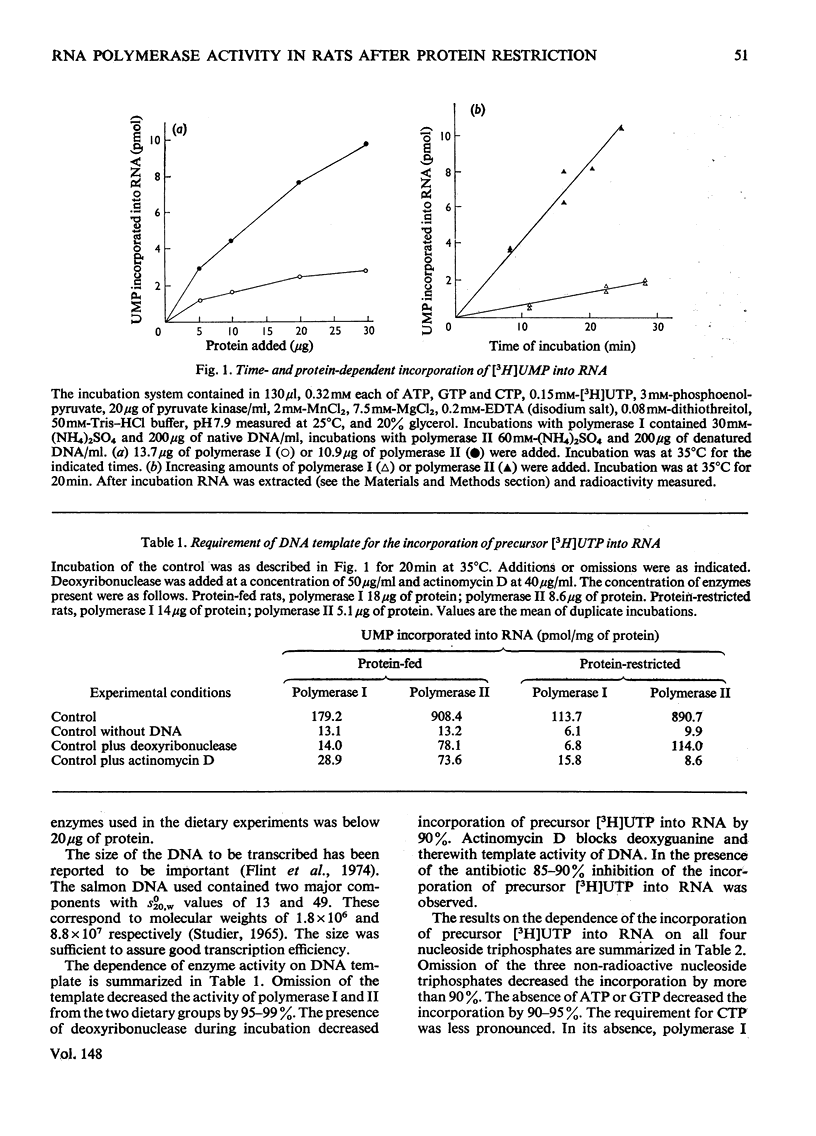
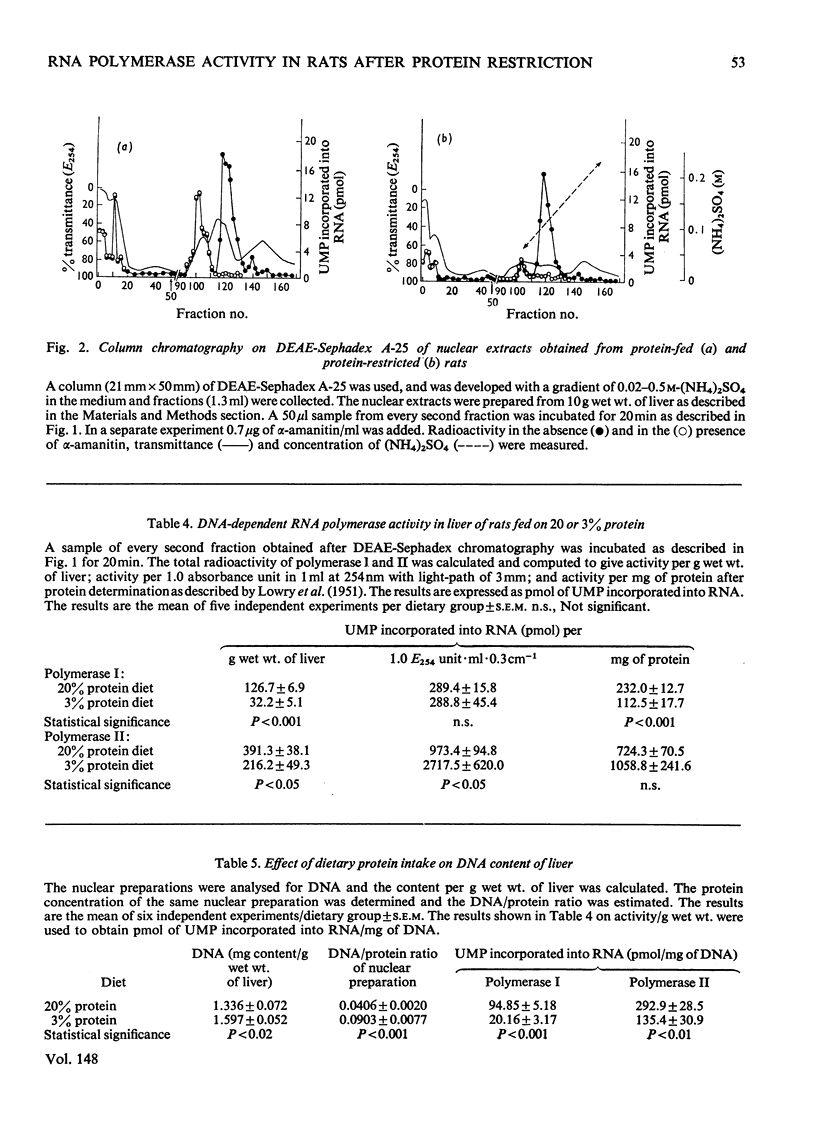
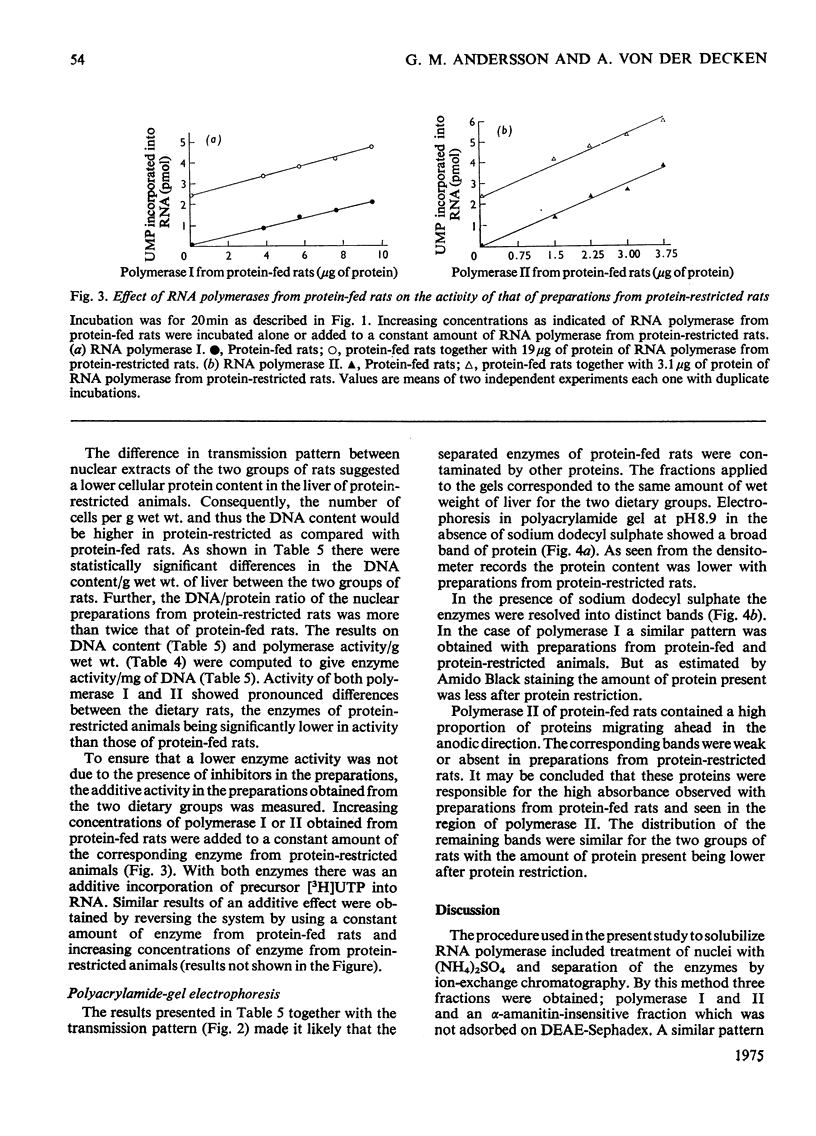
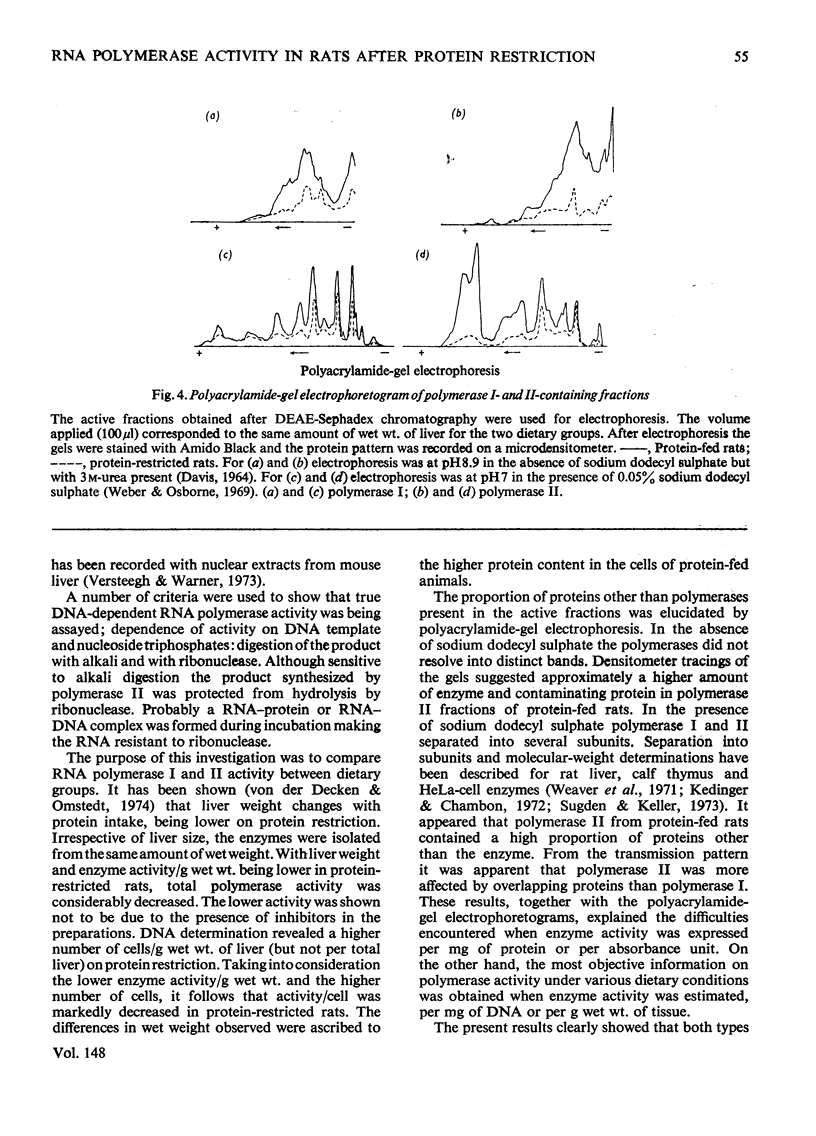
Rats were fed for 6 days on a diet containing either 3 or 20% high-quality protein. Nuclei were isolated from liver and DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (EC 2.7.7.6) extracted with 1 M-(NH4)2SO4. The proteins were then precipitated with 3.5 M-(NH4)2SO4 and after dialysis applied to a DEAE-Sephadex column. The column was developed with a gradient of (NH4)2SO4. Polymerase I separated well from alpha-amanitin-sensitive polymerase II. The enzyme activities were compared between the two dietary groups. Rats that had received 3% protein showed a lower polymerase I activity per g wet wt. of liver, per mg of DNA and per mg of protein. Polymerase II was lower in activity per g wet wt. of liver and per mg of DNA, but was higher per mg of protein. Polyacrylamide-gel electrophoretograms showed a higher proportion of contaminating proteins in polymerase II fractions isolated from 20%-protein-fed rats. The data explain the lower activity obtained per mg of protein in these rats. It is concluded that a decrease in dietary protein content from 20 to 3% induces a fall in content and specific activity of RNA polymerase I and II in liver.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chesterton C. J., Humphrey S. M., Butterworth P. H. Comparison of the multiple deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase forms of whole rat liver and a minimal-deviation rat hepatoma cell line. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):675–681. doi: 10.1042/bj1260675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Pfeiffer C., Sekeris C. E. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from insect tissue. FEBS Lett. 1972 Mar 15;21(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., De Pomerai D. I., Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. Template specificity of eucaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Effect of DNA structure and integrity. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. R. The effect of diet on rat liver nucelar DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Nutr Soc. 1972 Dec;31(3):291–295. doi: 10.1079/pns19720053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 3. Purification of calf-thymus BI and BII enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Comparative biochemistry of chondroitin sulphate-proteins of cartilage and notochord. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):37–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1250037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näslund P., Liljesvan B., Abrahamsson L. High-resolution analyzer of thermal denaturation. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omstedt P. T., von der Decken A. Functional instability of skeletal muscle ribosomes after protein restriction of rats. J Nutr. 1974 Aug;104(8):1061–1068. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.8.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roeder R. G. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Keller W. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. I. Purification and properties of an -amanitin-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase and stimulatory factors from HeLa and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3777–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versteegh L. R., Warner C. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases from normal mouse liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):838–844. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von der Decke A. Activation in vitro of rat liver polyribosomes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):138–147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Blatti S. P., Rutter W. J. Molecular structures of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (II) from calf thymus and rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2994–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3 in the transcription of the tRNA and 5S RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. Products of RNA polymerases in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Decken A. Modification of the in vitro amino acid incorporation capacity of rat liver after in vivo and in vitro treatments. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Decken A., Omstedt P. T. Dietary protein quality measured by in vitro protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle ribosomes. J Nutr. 1972 Dec;102(12):1555–1562. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.12.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Decken A., Omstedt P. T. Effect of dietary protein and amino acid mixture on protein synthesis in vitro in rat liver. Nutr Metab. 1974;16(6):325–336. doi: 10.1159/000175506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


