Extended Data Fig. 8 ∣. Tip contamination, sterilization and reuse.
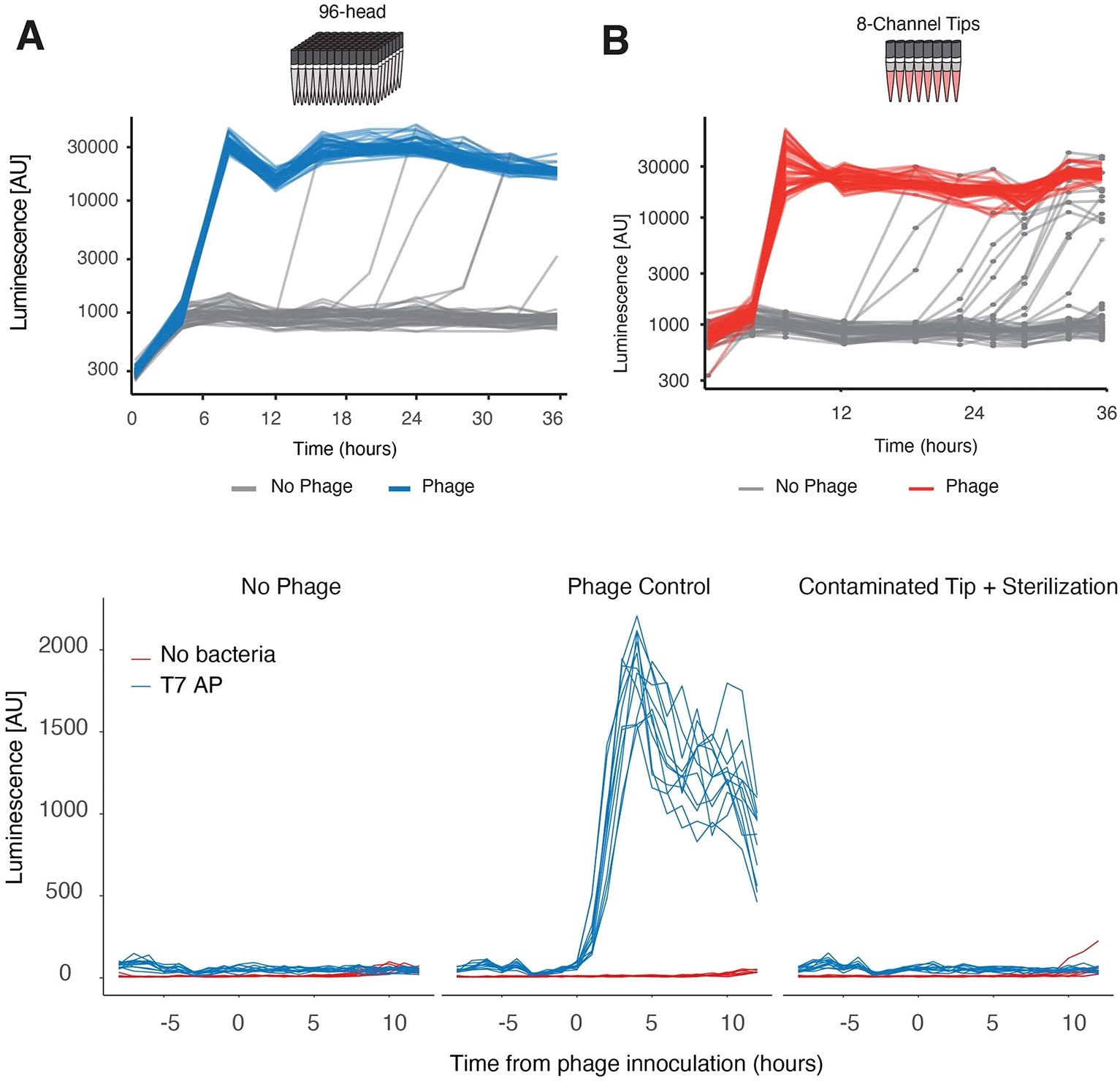
To assess the maximum amount of possible cross-contamination, T7 RNAP-containing phage were inoculated into cultures containing pT7-psp-LuxAB bacteria in a grid-like pattern with 48 phage-containing wells and 48 no-phage-containing wells. PRANCE steps were performed with either (a) the 96-head channel or (b) the 8-channel pipettor. Use of the 96-well head gave less cross-contamination events, which we attributed to lower fly-over events. (c) To assess the impact of tip-sterilization and reuse in the optimized robotic method and configuration (Supplemental Video 1), robotic tips were submerged in either water or T7 RNAP-containing phage and then sterilized prior to being used to maintain high-throughput bacterial cultures containing pT7-psp-LuxAB22. Sterilized tips were also used to propagate bacteria inoculated with T7 RNAP phage as a positive control to ensure that bleach carryover did not affect phage propagation. No cross contamination was observed in the serialized tip condition over 12 hours, indicating that tips could be reused for a minimum of 12 hours without being replaced.
