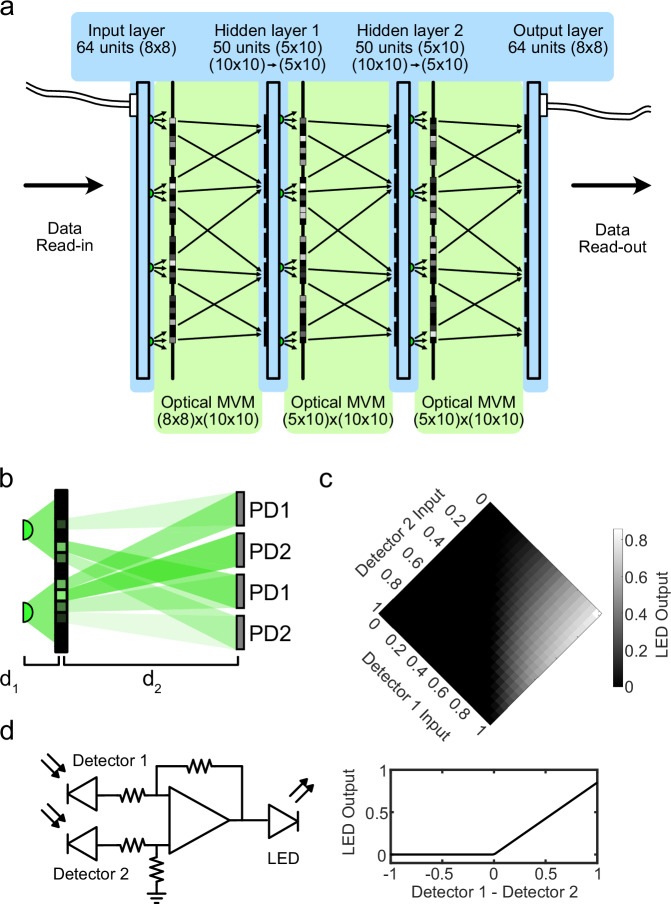
Fig. 2. Schematic of our multilayer optoelectronic neural network implementation with optical operations (green) and electronic operations (blue).
a Data is read-in electronically to an Input layer with 64 units arranged on an 8 × 8 array of LEDs. A fully connected matrix-vector-multiplication (MVM) maps light from these units to a 10 × 10 array of photodiodes (PDs). Hidden layer 1 combines pairs of values from the PDs to drive a 5 × 10 array of LEDs. A second MVM and hidden layer implement Hidden layer 2 and a third MVM is mapped onto an 8 × 8 array of PDs of the Output layer (partially reproduced from ref.53). b Ray-tracing illustrates how a fully connected MVM operation is performed. c Amplitude weights are nonnegative, and a pair of photodiodes are fed into an analog electronic circuit that performs a differencing operation before driving an LED. d Example output LED response to a pair of detector inputs. Negative currents in the circuit are truncated by the LED, effectively implementing a linear rectification (ReLU).