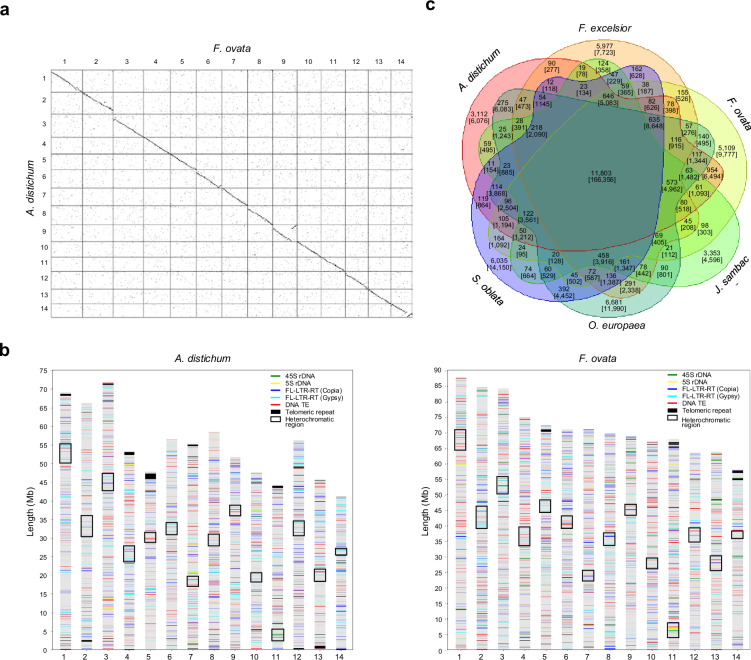
Fig. 2.
Chromosomal synteny, repetitive sequence distribution, and gene families in A. distichum and F. ovata. (a) Dot plot comparison of A. distichum and F. ovata pseudochromosome assemblies. Dots closest to the diagonal line reflect collinearity between the two assemblies. (b) Distributions of various repetitive sequences, including rDNA, FL-LTR-RTs, DNA TEs, and telomeric repeats. Black boxes indicate the location of repetitive sequence-enriched heterochromatic regions, and colored lines represent different types of repetitive sequences. (c) Venn diagram showing unique and shared gene families among six sequenced genomes of the Oleaceae family. The numbers of gene families and genes (in brackets) for each group are provided. The NCBI and China National Center for Bioinformation accession numbers are as follows: F. excelsior, GCA_900149125; J. sambac, GWHAZHY00000000; O. europaea, GCF_002742605; S. oblata, GWHBHRY00000000.