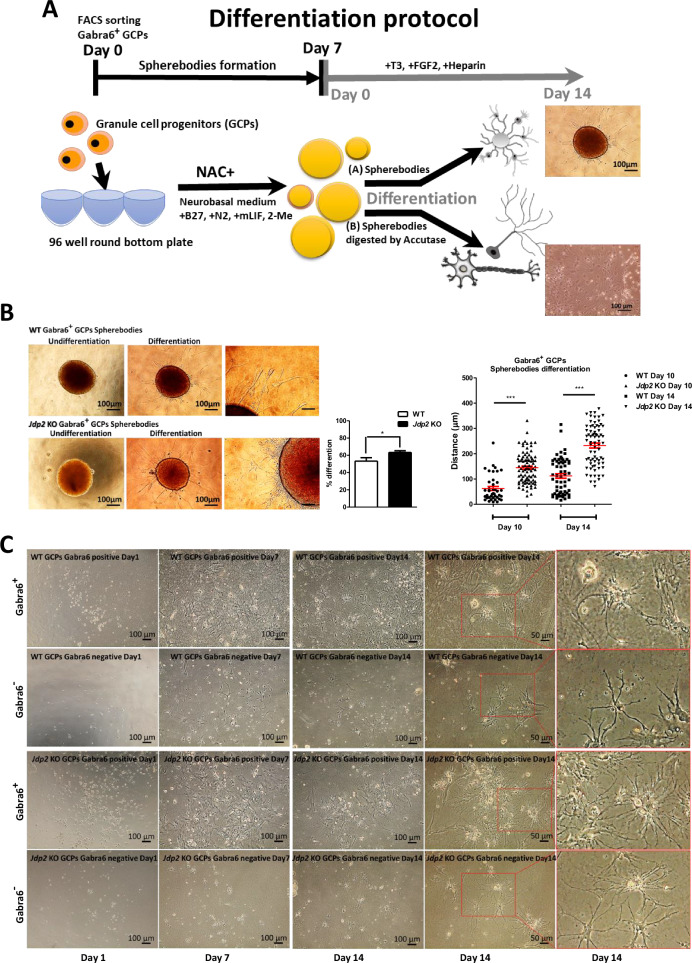
Fig. 3. Differentiation of Gabra6+ GCPs into neural cells.
A Two differentiation protocols of Gabra6+ GCPs were used: the sphere body method and the 2D-accutase culture method. A 96-well non-attached plate was used to generate sphere bodies, which were cultured in mouse GC medium supplemented with mLIF and 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME) for 7 days. Then, the spherebodies were transferred to a differentiation medium containing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin 3 (NT3), thyroid 3 (T3), and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), to induce Purkinje cells (PCs). The spherebodies were treated with accutase and plated in the 2D-plates and then committed to the differentiation as described in Materials and Methods. After 14 days, the differentiated cells were shown in respective panels. Scale bars: 100 and 50 μm. B Differentiation process of spherebodies derived from WT and Jdp2 KO Gabra6+ GCPs. Undifferentiated GCP sphere bodies (left) and differentiated GCP sphere bodies (middle and right) are shown. Scale bars, 100 and 50 μm. The quantitative ratio of the sphere bodies differentiated from WT (n = 43) and Jdp2 KO (n = 44) GCPs was measured. The neurite growth distance was measured on days 10 and 14. The Jdp2 KO GCPs exhibited longer neurites from differentiated sphere bodies compared with WT GCP-derived neurites (n = 5: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001). C The differentiation of WT and Jdp2 KO Gabra6+ GCPs was performed as described in the Materials and Methods. After digesting the respective sphere bodies with accutase, the cells were transferred into the differentiation medium and cultivated further for 1, 7, and 14 days. Two-dimensional (2D) cell cultivation from Jdp2 KO Gabra6+ GCPs yielded a greater number of dendrites compared with WT Gabra6+ GCPs. After 14 days of differentiation, the bright-field images showed the presence of Purkinje cells (PCs). The Purkinje cells were stained using neuronal markers, for quantification, as shown in Fig. 4B. Scale bars, 100 and 50 μm.