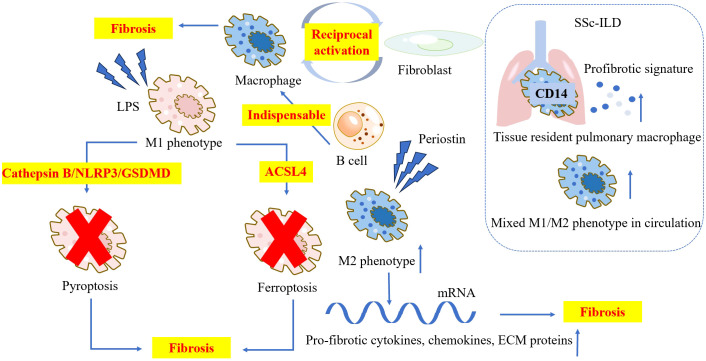
Figure 3.
The characteristic and pathogenetic roles of the macrophages in SSc. Macrophages and fibroblasts mutually activate each other and contribute to the pathology in SSc. B cells promote the differentiation of profibrotic macrophages, and is indispensable for the progression of SSc. Periostin induces higher ratio of M2 macrophage and upregulates the mRNA level of pro-fibrotic cytokines, chemokines, and ECM proteins. M1 macrophage facilitates fibrosis by pyroptosis and ferroptosis. CD14+ tissue resident pulmonary macrophages in SSc-ILD patients’ lungs show an active profibrotic signature. Elevated levels of mixed M1/M2 phenotype macrophages are observed in the circulation of SSc-ILD patients. ACSL4, Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member4; CD, cluster of differentiation; ECM, extracellular matrix; GSDMD, Gasdermin D; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3; SSc-ILD, systemic sclerosis-interstitial lung disease.