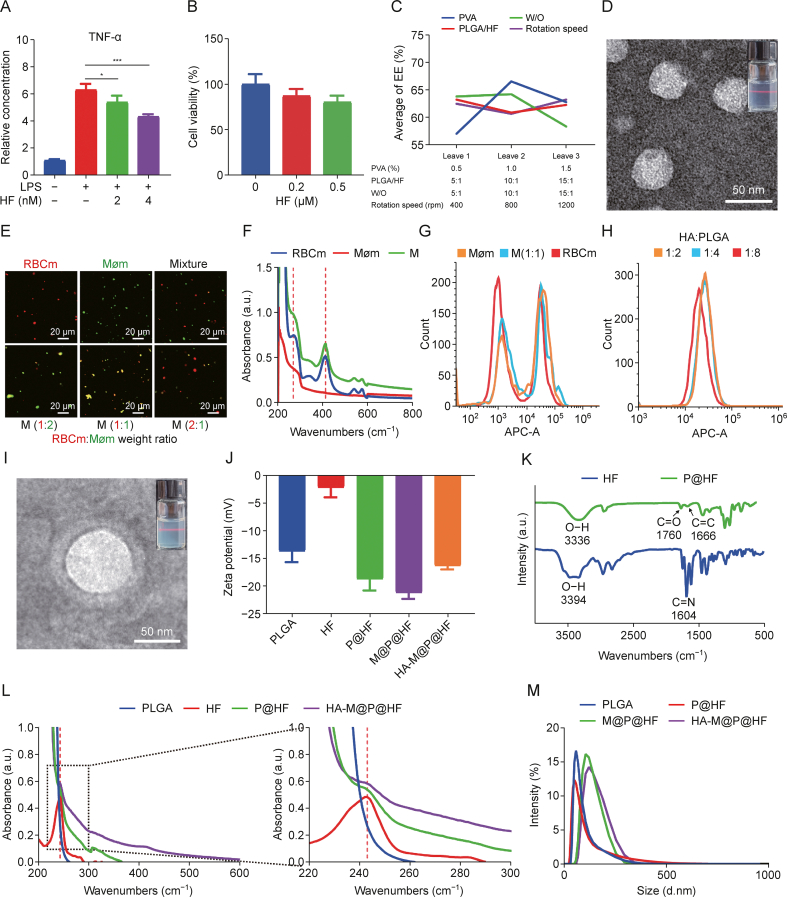
Fig. 2.
Preparation and characterization of hyaluronic acid (HA)-modified hybrid membrane (M)-camouflaged poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) loaded halofuginone hydrobromide (HF) nanoparticles (NPs) (HA-M@P@HF NPs). (A) In vitro inflammatory factor tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) of macrophages after HF (2 and 4 nM) treatment. (B) Cell viability of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes-rheumatoid arthritis (HFLS-RA) following incubation with HF (0.2 and 0.5 μM) for 48 h. (C) Orthogonal experimental design and statistical analysis. (D) Transmission electron microscope (TEM) image of P@HF NPs (inset: image of P@HF NPs solution). (E) Fluorescent images of red blood cell membrane (RBCm) and macrophage membrane (Møm) mixture, and M (red for RBCm and green for Møm). (F) Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) of RBCm, Møm, and M. (G) Flow cytometry profiles of Møm@P@chlorin e6 (Ce6), M@P@Ce6, and RBCm@P@Ce6 uptake in activated macrophages. (H) Flow cytometry profiles of activated macrophage uptake achieved by HA-M@P@Ce6 loaded with different proportions of targeted molecule HA. (I) TEM image of HA-M@P@HF NPs (inset: image of HA-M@P@HF NPs solution). (J) Potential measurement of different NPs. (K) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis of HF and P@HF. (L) UV-vis absorption spectra of HF, PLGA, P@HF, and HA-M@P@HF NPs. (M) Hydrodynamic size distribution of various NPs. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; EE: entrapment efficiency; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; W/O: water-to-oil ratio; APC-A: a allophycocyanin-area.